Time limit: 0
Quiz Summary
0 of 39 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Quiz complete. Results are being recorded.
Results
0 of 39 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 39
1. Question
A 52-year-old man comes to the office with concerns about a “heart problem.” Three years ago, the patient was told during a routine physical examination that he had a heart murmur. Currently, he has no specific complaints, but he mentions that he has become tired more easily in the past year. He has no chest pain or lower extremity swelling or significant medical history. The patient was healthy as a child and received all his childhood vaccinations. Blood pressure is 145/90 mm Hg and pulse is 80/min and regular. Physical examination reveals a holosystolic murmur best heard at the apex of the heart that radiates to the axilla. The lungs are clear on auscultation and abdominal examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is the best indicator of the severity of this patient’s valve disease?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 39
2. Question
A 32-year-old woman comes to the office due to progressive exertional dyspnea and easy fatigability. She immigrated to the United States from India several years ago and reports a history of rheumatic fever during her childhood. Cardiac auscultation reveals a diastolic high-frequency sound and a rumbling diastolic murmur heard best in the left fifth intercostal space at the midclavicular line. Cardiac catheterization is performed for hemodynamic evaluation, and the results are represented below. Timing of the high-frequency sound heard during cardiac auscultation of this patient best corresponds to which of the following letters?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 39
3. Question
A 63-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to increasing dyspnea. He was unable to mow his lawn the previous day due to shortness of breath. The patient has a history of hypertension and a 20-pack-year smoking history. He is retired and traveled to Hawaii 2 months ago. Blood pressure is 160/86 mm Hg, pulse is 94/min, and respirations are 24/min; oxygen saturation is 94% on room air. Physical examination reveals bilateral lung crackles and occasional wheezes. Laboratory testing reveals elevated brain natriuretic peptide levels. Which of the following is the primary trigger for the release of this substance in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 39
4. Question
A 16-year-old previously healthy boy is brought to the office due to palpitations. He was watching a documentary at a movie theater when his heart suddenly began to race and he became lightheaded. The patient says that he has felt “rapid heartbeats” in the past and thought that they were due to stress from school exams, but he has never had associated lightheadedness before. He has no chest pain or dyspnea. Physical examination is within normal limits. ECG strip is shown in the exhibit. Which of the following is most likely to be seen in this patient?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 39
5. Question
A 54-year-old man comes to the office due to light-headedness when walking his dog in the morning. He has had no chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness, or headaches. Cardiac auscultation findings at the right sternal border are heard in the exhibit. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s symptoms?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 39
6. Question
A 34-year-old woman is being evaluated for fatigue and progressive exertional dyspnea. She goes mountain biking with friends a few times a month and recently noticed that she has to stop and rest more frequently when traveling uphill. The patient has no significant medical history and takes no medications. She occasionally drinks alcohol but does not use tobacco or illicit drugs. Her father died of a myocardial infarction at age 72. Lung auscultation is normal. An echocardiogram shows an enlarged coronary sinus. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the observed finding in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 39
7. Question
A 77-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department with severe lightheadedness and near-syncope that began earlier in the day. Over the past several months, she has experienced occasional episodes of lightheadedness and feeling unsteady, which she attributed to “old age.” The patient has not had chest pain, shortness of breath, or lower extremity swelling. She was diagnosed with hypertension 10 years ago and has been taking losartan. The patient does not take any other medications. She lives alone and is independent in her daily activities. An ECG obtained in the emergency department is shown in the exhibit. Cell degeneration in which of the following locations is most likely responsible for this patient’s current condition?
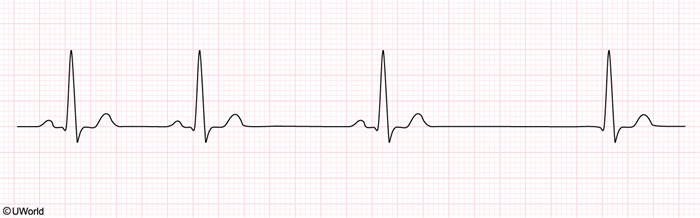 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 39
8. Question
A 33-year-old woman who recently immigrated to the United States is brought to the emergency department with severe shortness of breath and hemoptysis. Physical examination reveals a diastolic murmur. Chest x-ray shows severe pulmonary vascular congestion and edema. She is admitted to the hospital, treated with diuretics, and begins to feel better. However, during her hospitalization, she develops right-sided hemiparesis. Which of the following additional findings in this patient would be most suggestive of combined disease involving the mitral and aortic valves rather than exclusive mitral involvement?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 39
9. Question
A 73-year-old man is evaluated for exertional dyspnea. His exercise tolerance has decreased over the last year, and he can barely walk 2-3 blocks without stopping. The patient also reports occasional episodes of lightheadedness and palpitations. He has had no chest pain or syncope. He was diagnosed with hypertension in the past but does not take any medications. Physical examination reveals a cardiac murmur. The patient is referred to a cardiologist for further evaluation. Cardiac catheterization is performed, and the findings are shown in the image below. Which of the following points most likely corresponds to the peak murmur intensity in this patient?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 39
10. Question
A 54-year-old woman comes to the office due to exertional dyspnea and fatigue. The patient gets short of breath while walking to a store 2 blocks away from her home. She also has trouble breathing at night and sleeps with 2 or 3 pillows to prop her up. She has had occasional palpitations but no chest pain. The patient takes no medications on a regular basis, and does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. After initial evaluation, she is scheduled for a left heart catheterization, the findings of which are shown below.

Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 39
11. Question
A 2-month-old boy is found unresponsive in his crib. He had previously been well and had a normal physical examination at his 2-month visit approximately 1 week earlier. An autopsy is performed to determine the cause of death. The pathologist concludes that the infant likely died of sudden infant death syndrome. The autopsy also shows an incidental finding of bicuspid aortic valve. If this patient had survived, he would have been at greatest risk for which of the following events?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 39
12. Question
A 34-year-old Russian immigrant comes to the office with a 2-month history of exertional dyspnea and progressive lower extremity swelling. He also reports abdominal distension and decreased appetite. The patient has gained 4.5 kg (9.9 lb) over the last 2 months. Medical history is significant for hypertension and recurrent lung infections requiring prolonged antibiotic therapy. The patient has no history of coronary artery disease. He has smoked a pack of cigarettes daily for the past 15 years. The patient undergoes noninvasive cardiac testing, followed by cardiac catheterization. A jugular venous pressure tracing is shown in the image below:

Item 1 of 2
The waveform indicated by the arrow most likely corresponds to which of the following?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 39
13. Question
Item 2 of 2
The patient is admitted to the hospital for further work-up and treatment. After initial evaluation, CT scan of the chest is obtained and is shown in the image below:
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 39
14. Question
A 44-year-old man with a history of intravenous drug use came to the emergency department due to fever and chills. Multiple blood culture sets were positive for Staphylococcus aureus, and the patient was diagnosed with infective endocarditis. He was successfully treated with a long course of antibiotics. Six months later, he returns to the clinic for a follow-up evaluation. The patient has no symptoms and reports good exercise tolerance. He is afebrile, blood pressure is 140/62 mm Hg, pulse is 82/min, and respirations are 16/min. Chest auscultation reveals a decrescendo diastolic murmur over the third intercostal space along the left sternal border. Echocardiogram shows severe aortic regurgitation, likely as a sequela to the prior infection. Which of the following changes is most responsible for maintaining cardiac output in the setting of this valvular abnormality?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 39
15. Question
A 71-year-old man comes to the office due to a 2-month history of progressive exertional dyspnea. The patient is unable to walk half a block without resting and can no longer climb stairs without stopping every few steps. He also has had difficulty sleeping due to repeatedly waking up at night feeling like he is suffocating. Physical examination shows bilateral lower extremity edema and distended neck veins. Cardiac auscultation findings over the apex are given below. This patient’s auscultatory findings most likely reflect which of the following?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 39
16. Question
A 68-year-old man comes to the office due to exertional shortness of breath and fatigue, which have progressed over the past year. The patient has a history of hypertension, but medical history is otherwise unremarkable. He is a lifetime nonsmoker. His father died of a “heart attack” at age 70. Blood pressure is 144/74 mm Hg, and pulse is 72/min and regular. Cardiac auscultation reveals a 3/6 ejection-type, late-peaking systolic murmur and a barely audible S2. The murmur diminishes in intensity during the straining phase of the Valsalva maneuver. Which of the following processes underlies this patient’s current condition?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 39
17. Question
A 37-year-old man is found unresponsive under a tree during a thunderstorm. He is not breathing when paramedics arrive on the scene. On examination, his pupils are fixed and dilated. Several cutaneous erythematous marks in a fern-leaf pattern are seen on his lower extremities. Second-degree burns are present on both arms. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is started; however, the patient does not respond and is pronounced dead on arrival at the hospital. Which of the following is most likely to be the primary cause of his death?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 18 of 39
18. Question
A 35-year-old primigravid woman comes to the clinic during the second trimester. The patient reports that she has had some tiredness, which she attributes to pregnancy. She takes 1 nap during the day. She has no chest pain, cough, or lower extremity swelling. As a child, the patient was told that she has a murmur but does not know any details and says that she has felt well until recently. On physical examination, a 3/6 midsystolic murmur is heard at the left upper sternal border and S2 is widely split. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 39
19. Question
A 54-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to severe shortness of breath and palpitations. During initial assessment, pulse oximetry shows 83%. Diffuse, bilateral crackles are heard on lung auscultation. Chest x-ray is consistent with pulmonary edema. ECG shows atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response. The patient dies despite appropriate medical care. Autopsy is performed and gross examination of the heart is shown below.

Histologic examination of the myocardial tissue reveals thick myocardial fibers with large, hyperchromatic nuclei as well as mild interstitial fibrosis. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 39
20. Question
A 10-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department due to shortness of breath and palpitations for the past day. He also has associated fever and fatigue. Vital signs indicate tachypnea, tachycardia, and hypotension. On cardiac auscultation, the patient has a new holosystolic murmur. He is admitted to the hospital for further workup and management. A cardiac biopsy is performed due to decompensation and an unclear diagnosis. Light microscopy of the tissue specimen is shown in the image below.

Which of the following most likely preceded development of this patient’s current condition?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 21 of 39
21. Question
A 75-year-old man comes to the office due to worsening dyspnea and fatigue on exertion over the last 6 months. Recently, he has had severe lightheadedness during physical activity. Blood pressure is 125/65 mm Hg and pulse is 65/min and regular. Physical examination reveals a harsh ejection-type systolic murmur at the base of the heart radiating to the neck. The second heart sound is diminished in intensity. A fourth heart sound is heard at the cardiac apex. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s heart condition?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 22 of 39
22. Question
A 21-year-old man comes to the emergency department following an episode of syncope. The syncopal episode was not provoked by any activity or circumstance, nor was it preceded by lightheadedness. The patient has no significant past medical history and he is not taking any medications. An ECG obtained in the ER reveals QT-interval prolongation but is otherwise unremarkable. Assuming this is an inherited condition, the relevant mutation most likely affects which of the following structures?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 23 of 39
23. Question
A 74-year-old man comes to the office for a follow-up visit for hypertension. His last visit was a year ago. He has no chest pain, shortness of breath, leg swelling, or dizziness. The patient is compliant with his medications and can tolerate a moderate level of physical activity. Blood pressure is 145/75 mm Hg and pulse is 67/min and regular. Auscultation findings at the base of the heart are depicted in the exhibit below.

Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s physical findings?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 24 of 39
24. Question
A 6-year-old boy is evaluated in the office for difficulty hearing. The patient has no ear pain, discharge, or upper respiratory symptoms. Initial testing suggests that he has bilateral sensorineural hearing loss. He has no motor deficits or cerebellar signs. His paternal uncle died suddenly at age 12. Examination of the ears, nose, and throat is normal. ECG shows normal sinus rhythm with a prolonged QT interval (520 msec). Echocardiogram shows normal left and right ventricular function with no significant valvular disease. A genetic defect affecting which of the following is most likely present in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 25 of 39
25. Question
Cardiac catheterization is performed on a 7-year-old boy. The image below shows the pattern of oxygen saturation in the patient’s cardiac chambers and outflow tracts (structural abnormalities are not shown).

This patient most likely has which of the following findings on physical examination?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 26 of 39
26. Question
A 72-year-old man with long-standing dyspnea was seen in the clinic after experiencing an episode of syncope. Physical examination showed weak and slowly rising arterial pulses. Cardiac auscultation showed a harsh midsystolic murmur best heard at the second right intercostal space with decreased intensity of the second heart sound. Electrocardiogram and echocardiogram confirmed the diagnosis of severe aortic stenosis. Two months later, the patient comes to the emergency department with palpitations and increased shortness of breath. His blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg and his heart rate is 130/min with an irregularly irregular rhythm. Electrocardiogram shows new-onset atrial fibrillation without significant ST-segment or T-wave changes. Chest x-ray shows bilateral pulmonary edema. Which of the following hemodynamic changes is most likely associated with this patient’s current presentation?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 39
27. Question
A 65-year-old man with a long history of hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus comes to the office for a routine checkup. The patient is a former smoker with a 15-pack-year history. He jogs 3 miles per day. BMI is 28.5 kg/m2. Family history is unremarkable. Auscultation findings over the cardiac apex are given below. The auscultation findings are best explained by which of the following?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 28 of 39
28. Question
A 34-year-old man comes to the office due to heart palpitations that are particularly prominent at night. With moderate exertion he also experiences head-pounding accompanied by involuntary head-bobbing. The patient recently emigrated from Southeast Asia and remembers being diagnosed with a heart murmur years before, but he cannot recall the type of murmur and has never received any treatment. He has no other medical conditions and takes no medications. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. The patient’s father has coronary artery disease and his mother has type 2 diabetes mellitus. Based on this patient’s history, which of the following findings is most likely to be present on further evaluation?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 29 of 39
29. Question
A 78-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to acute vision loss. She had rapid-onset monocular vision loss in the left eye that developed over an hour. There is no associated pain in the eye, but the patient has had left-sided headaches most days for the last 3 weeks. She also has had achy pain in the shoulders that has slowly worsened over the last month. Examination shows decreased pupillary light reflex in the left eye with severely impaired visual acuity. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for this patient’s condition?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 30 of 39
30. Question
A 64-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to worsening dizziness and shortness of breath for the past several days. The patient was diagnosed with advanced stage lung cancer 6 months ago and is receiving palliative care. The patient has no other medical history. Blood pressure is 85/45 mm Hg, pulse is 122/min and regular, and respirations are 22/min. Pulse oximetry is 94% on room air. There are undulations in blood pressure at different phases of respiration. On physical examination, the point of maximal impulse is not palpable, and heart sounds are distant. Chest x-ray reveals diffuse pulmonary metastatic disease and new enlargement of the cardiac silhouette. Which of the following hemodynamic changes are most likely present in this patient due to his current cardiac condition?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 31 of 39
31. Question
A 72-year-old man comes to the office due to palpitations and mild fatigue for the last 3 weeks. He has otherwise been feeling well. The patient walks 2 miles around his neighborhood twice per week with no chest pain or shortness of breath. Medical history is remarkable for benign prostatic hyperplasia, for which he takes terazosin. He drinks 1-2 cups of coffee every day and a glass of wine once or twice per month. Temperature is 37 C (98.6 F), blood pressure is 128/68 mm Hg, and pulse is 78/min and irregular. Physical examination reveals a 2/6 early-peaking systolic murmur at the right upper sternal border. Carotid pulses are prompt and full bilaterally. The lungs are clear to auscultation. There is no peripheral edema. ECG is shown in the exhibit. Which of the following is most likely the strongest risk factor for this patient’s presentation?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 32 of 39
32. Question
A newborn girl is evaluated in the nursery for a heart murmur. The infant was born at 39 weeks gestation via spontaneous vaginal delivery following an uncomplicated pregnancy. She has been breastfeeding well and has urinated 3 times and stooled once. Approximately 1 hour after delivery, a 2/6 systolic murmur could be heard at the left upper sternal border. At age 8 hours, the murmur could be heard during both systole and diastole. Examination at age 24 hours revealed no murmur. Which of the following is most likely responsible for the disappearance of this patient’s murmur?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 33 of 39
33. Question
A 29-year-old woman, gravida 1 para 0, at 28 weeks gestation comes to the office to establish prenatal care after recently moving to a new city. She has had no complications in this pregnancy and had a normal anatomy ultrasound at 20 weeks gestation. On physical examination, the fundal height measures 28 cm. Cardiac auscultation reveals a 2/6 blowing systolic murmur best heard at the left sternal border. The murmur intensifies with inspiration, and there is no ejection click or palpable thrill at the sternal notch. The lungs are clear to auscultation. There is 1+ pitting edema to the midshins bilaterally. Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient’s murmur?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 34 of 39
34. Question
A 5-week-old boy is receiving care in the neonatal intensive care unit. The patient was born at 26 weeks gestation with a birth weight of 0.79 kg (1 lb 10 oz). Echocardiography reveals a patent ductus arteriosus and a dilated left atrium. The patient has moderate pulmonary edema. During surgical ligation of the ductus arteriosus, the surgeons perform a left-sided thoracotomy, visualize the ductus, and place a small metal clamp across the vessel. Which of the following changes is most likely to take place immediately after ligation?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 35 of 39
35. Question
A full-term newborn is evaluated in the delivery room due to mild tachypnea and cyanosis immediately after birth. Fetal ultrasonography performed during pregnancy revealed transposition of the great arteries. Heart rate and blood pressure are normal. Oxygen saturation is 72%. Cyanosis is apparent in the hands, feet, lips, and tongue. Peripheral pulses are strong. Bedside echocardiography confirms the prenatal diagnosis; there is also a small patent foramen ovale and a small patent ductus arteriosus. Definitive surgical correction of the main congenital abnormality is planned. Pending definitive repair, which of the following temporary measures would be most likely to improve this patient’s condition?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 36 of 39
36. Question
A 62-year-old woman with no significant medical history is brought to the emergency department due to fatigue and substernal chest pain that began 6 hours ago. On arrival, ECG is consistent with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Coronary angiography shows right-dominant coronary circulation and a thrombotic occlusion of the proximal right coronary artery, which supplies blood to the patient’s right ventricle and the inferior and posterior portions of the left ventricle. A drug-eluting stent is placed, and she is discharged 2 days later without complication. After 6 weeks, the patient follows up in the clinic and undergoes echocardiography that shows left ventricular contractile dysfunction with normal right ventricular function. Which of the following characteristics of the right ventricle compared to the left ventricle best explains these echocardiography findings?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 37 of 39
37. Question
An 8-hour-old boy is being assessed for a murmur in the newborn nursery. The patient was born at 37 weeks via cesarean delivery. Apgar scores were 7 and 8 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. He was noted to have a harsh ejection systolic murmur of 4/6 intensity during initial newborn examination. Brachial and femoral pulses are 2+ with no delay. While the patient is breastfeeding for the first time, his face, lips, hands, and feet become cyanotic. The murmur cannot be heard during the cyanotic episode. Which of the following oxygen saturation percentages are most likely present during the cyanotic episode?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 38 of 39
38. Question
A 52-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to increasing dyspnea and chest tightness over the past 2 weeks. She has a history of stage 4 chronic kidney disease due to chronic glomerulonephritis. Temperature is 36.6 C (97.8 F), blood pressure is 106/82 mm Hg, and pulse is 98/min. Systolic blood pressure decreases by 12 mm Hg during inspiration. Physical examination shows distant heart sounds and clear lungs. Echocardiography in this patient is most likely to reveal which of the following findings?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 39 of 39
39. Question
A 6-month-old girl is brought to the office for her first visit after being adopted from another country a week ago. The parents notice that she often seems to breathe hard and fast, particularly after feeding or crying. Her lips sometimes turn blue, as well. On examination, height and weight are at the 15th and 2nd percentiles, respectively. The patient has a 4/6, harsh systolic, crescendo-decrescendo murmur best heard at the left upper sternal border. Complete blood count shows:
Hematocrit
52%
Platelets
240,000/mm3
Leukocytes
11,000/mm3
Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this patient’s elevated hematocrit?
CorrectIncorrect
