Time limit: 0
Quiz Summary
0 of 21 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Quiz complete. Results are being recorded.
Results
0 of 21 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 21
1. Question
A 68-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department due to worsening fever, cough, and confusion. The patient has had a “cold and congestion” since last week, which initially improved, but she began feeling worse again 3 days ago. Her daughter reports that the patient has also been eating poorly. Other medical conditions include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and chronic kidney disease. Temperature is 39.4 C (102.9 F), blood pressure is 74/46 mm Hg, pulse is 128/min, and respirations are 30/min. Oxygen saturation is 94% on 2 L/min. On physical examination, the patient is lethargic with dry mucous membranes and flat neck veins. Lung examination reveals dullness to percussion and crackles at the right base. Chest x-ray shows a right lower lobe consolidation. Intravenous access is established. Intravenous administration of which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 21
2. Question
A 32-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to sudden-onset left-sided facial droop and arm weakness. The patient also has had right leg swelling after a recent road trip. She has no chronic medical conditions, and her only medication is an oral contraceptive. CT scan of the head shows a right middle cerebral artery territory acute infarction. Lower extremity ultrasound examination reveals a right femoral vein thrombus. No obvious cardiac structural abnormalities are detected on an echocardiogram. Agitated normal saline is injected into a peripheral vein to evaluate for abnormal right-to-left shunting. No bubbles are seen in the left side of the heart after several minutes. Which of the following is most appropriate to increase right-sided heart pressure to reveal an obscure intracardiac shunt?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 21
3. Question
A 26-year-old man collapsed while playing basketball and could not be resuscitated. Prior to the episode, he had exertional dyspnea and lightheadedness. Autopsy is performed. The lungs are completely normal. The heart is shown in the exhibit. If the patient had been examined prior to death, which of the following would most likely have been present?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 21
4. Question
Researchers are studying the coronary circulation in various healthy and diseased states. They measure blood flow and pressure (blue circle) in one of the epicardial coronary arteries of an experimental animal with cardiovascular physiology similar to that of humans. Then they clamp the artery to simulate 60% atherosclerotic stenosis and remeasure the flow and pressure distal to the lesion. Which of the following changes are most likely to be observed once steady state is achieved?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 21
5. Question
A 32-year-old woman comes to the outpatient clinic due to shortness of breath for the past 6 months. The patient says she can walk only 3-4 blocks on level ground before feeling out of breath. She also has an occasional dry cough at night. The patient denies any chest pain, palpitations, syncope, weight loss, or lower extremity swelling. She immigrated from Guatemala 8 years ago. Medical history is unremarkable. On physical examination, the patient appears comfortable. Blood pressure is 128/75 mm Hg and pulse is 78/min and regular. Peripheral pulses are full and symmetric. The lungs are clear on auscultation. S1 is loud. With the patient positioned on her left side and breath held at the end of expiration, a diastolic murmur is heard at mid- and end diastole. Otherwise, examination is unremarkable. Which of the following are the most likely left ventricular hemodynamic findings at rest in this patient?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 21
6. Question
A 12-day-old girl is evaluated in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) due to a murmur. The patient was born at 25 weeks gestation and was admitted to the NICU for respiratory support. She was born to a 21-year-old primigravida whose pregnancy was complicated by preeclampsia. Cardiac auscultation reveals a continuous murmur at the left sternal border, and bounding femoral and palmar pulses are palpable. Echocardiography confirms the diagnosis. Compared with a normal infant, this patient most likely has which of the following changes in cardiac parameters?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 21
7. Question
A 70-year-old man comes to the office due to palpitations. He has felt an irregular and fast heartbeat on multiple occasions over the last month. The patient has not had chest pain, dyspnea, dizziness, or weakness. His medical history includes hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Temperature is 36.7 C (98.1 F), pulse is 102/min and irregular, blood pressure is 140/82 mm Hg, and respirations are 16/min. Cardiopulmonary auscultation reveals clear lungs and no heart murmurs. ECG shows an irregularly irregular rhythm with absent P waves. The patient is started on metoprolol and apixaban. Which of the following is likely to be directly affected as the result of this therapy?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 21
8. Question
A 2-year-old, previously healthy boy is brought to the emergency department due to a 4-day history of poor feeding, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. The patient has had 5-7 bowel movements every day for the past 4 days. Temperature is 36.8 C (98.2 F) and blood pressure is 65/42 mm Hg. On physical examination, the patient is lethargic. Mucous membranes are dry, and the eyes are sunken. The lungs are clear to auscultation. No murmurs are heard. Abdominal examination shows distension and tenderness; bowel sounds are hyperactive throughout. Which of the following changes is most likely present in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 21
9. Question
A 28-year-old professional endurance athlete comes to the office after his team physician detected a heart murmur. The patient has no symptoms and has no exercise limitations. Medical history is nonsignificant. Blood pressure is 110/66 mm Hg and pulse is 54/min. Physical examination shows a soft systolic murmur best heard at the left second intercostal space in the supine position. The murmur disappears when the patient is upright but reappears after brief exercise. Which of the following cardiovascular adaptations best explains this patient’s finding?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 21
10. Question
A 65-year-old woman is brought to the hospital due to sudden-onset chest heaviness and shortness of breath that began an hour ago. Her medical history is significant for type 2 diabetes mellitus, obesity, and hypertension. Temperature is 36.7 C (98.1 F), blood pressure is 80/50 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 20/min. Extremities are cold and clammy. Diaphoresis is present. ECG shows ST-segment elevation in the lateral leads. Which of the following hemodynamic changes are most likely present in this patient?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 21
11. Question
Researchers conduct an experiment to determine hemodynamic changes during exercise. Invasive monitoring of various parameters is performed to obtain a left ventricular pressure-volume loop. Compared to at rest, which of the following changes is most likely to be observed during moderate to heavy exercise?
(solid line: at rest; dashed line: during exercise)
A.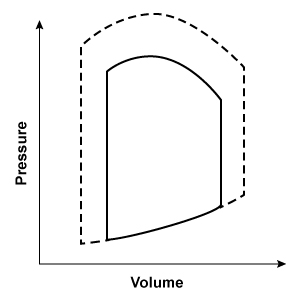 B.
B.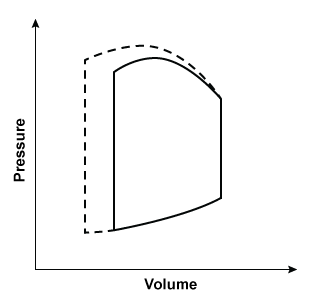 C.
C.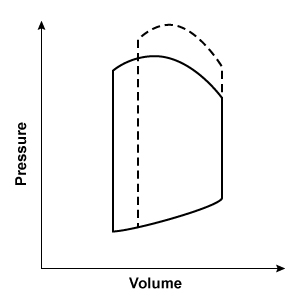 D.
D.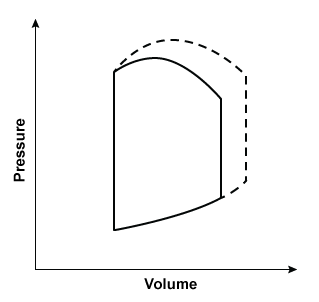 E.
E. CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 21
12. Question
A 14-year-old girl is brought to the office to establish medical care. The patient recently immigrated to the United States with her parents from Vietnam. Vital signs are within normal limits. Phonocardiogram obtained at the left upper sternal border is shown below.

Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient’s heart murmur?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 21
13. Question
A 17-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department after passing out. The patient was standing behind the dugout watching his friends play baseball when he suddenly felt warm and light-headed. Then he remembers awakening on the ground. Bystanders reported that the patient was unresponsive for approximately 2 minutes. He feels fatigued but does not have chest pain or shortness of breath. The patient has no significant medical history and does not use alcohol or drugs. Temperature is 36.7 C (98.1 F), supine blood pressure is 105/60 mm Hg and standing blood pressure is 110/65 mm Hg, pulse is 84/min, and respirations are 16/min. Pulse oximetry is 100% on room air. The patient is awake and alert. Pupils are equal and reactive. Heart and lung examinations are normal. The abdomen is soft and nontender. Neurologic examination is normal. ECG is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s syncope?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 21
14. Question
A 4-week-old boy undergoes cardiac catheterization for closure of a patent ductus arteriosus. The patient was born at 26 weeks gestation due to placental abruption. He has been cared for in the neonatal intensive care unit since delivery. Pulse oximetry shows 99% in the right hand and left foot. Echocardiography shows a moderately sized patent ductus arteriosus. After catheterization but before closure, blood gases are obtained from several locations. Compared with the partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) of a normal infant, this patient would be expected to have a higher PaO2 in which of the following locations?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 21
15. Question
A 6-week-old infant is brought to the office due to difficulty feeding. The patient was born at 39 weeks gestation via spontaneous vaginal delivery. He is breastfeeding for 5 minutes per side every 3 hours. The patient has profuse sweating and difficulty breathing with feeds. Weight is at the 5th percentile. On examination, the patient is tachypneic. Cardiac examination shows a holosystolic murmur at the left lower sternal border; a palpable thrill is present at the left sternal border. Compared to a healthy infant, this patient likely has which of the following intracardiac pressure changes?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 21
16. Question
A healthy 80-year-old man has participated in a longitudinal study over the past 30 years to study the effects of aging on overall cardiovascular status. He has undergone annual testing with echocardiography and his left ventricular ejection fraction has remained stable throughout the 30 years. Which of the following changes is most likely responsible for the preserved left ventricular ejection fraction in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 21
17. Question
A 28-year-old man comes to the emergency department with a 3-day history of increasing chest tightness and intermittent sharp chest pains. He also reports mild dyspnea, especially on exertion. The patient has no prior chronic medical conditions but had an upper respiratory illness a week ago that resolved without treatment. ECG reveals sinus tachycardia and low voltage QRS complexes that vary in the amplitude from beat to beat. Which of the following is the most likely chest x-ray finding in this patient?
A.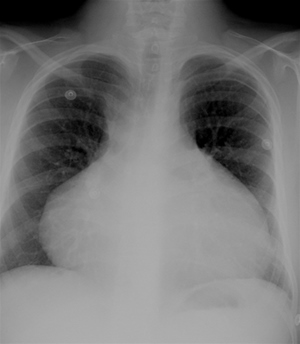 B.
B.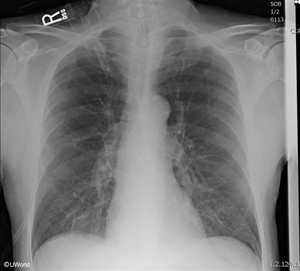 C.
C.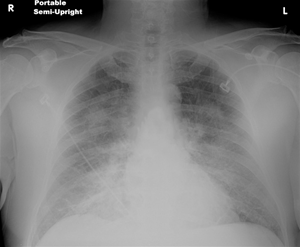 D.
D.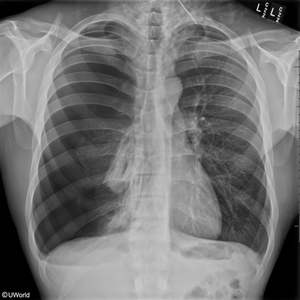 E.
E.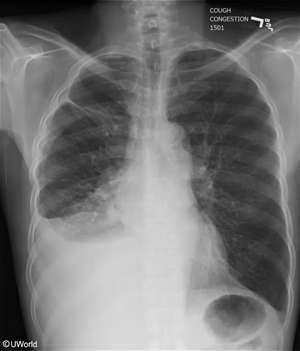 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 18 of 21
18. Question
An autopsy is being performed on a 72-year-old man with a history of myocardial infarction. Light microscopy of a portion of the left ventricle reveals the findings shown in the image below:

This patient most likely sustained the myocardial infarction during which of the following time frames prior to his death?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 21
19. Question
An 8-month-old previously healthy infant is brought to the urgent care clinic due to vomiting and watery diarrhea for the past 3 days. He attends a day care where recently several other children had similar symptoms. His mother states that the infant is less active and has no interest in feeding. Physical examination shows a listless infant with tachycardia, dry mucous membranes, and decreased skin turgor. The abdomen is nontender with hyperactive bowel sounds. Compared to pre-illness levels, which of the following sets of laboratory findings are most likely present in this patient?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 21
20. Question
A 30-year-old man is brought to the emergency department due to left-sided weakness. His left arm was sluggish after awakening, and he had difficulty walking to the bathroom. The patient has no known medical conditions but has a 2-month history of positional dyspnea. Vital signs are within normal limits. On examination, strength of the left upper and left lower extremity is reduced, and touch/temperature sensation is similarly diminished. Cardiovascular examination reveals an intermittent murmur at the apex without carotid bruits. Echocardiography shows a mobile, 3-cm left atrial mass obstructing the mitral opening during diastole. Histologic examination of this mass would most likely show which of the following findings?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 21 of 21
21. Question
A 32-year-old man dies suddenly in his sleep. An autopsy is performed and the heart is examined for signs of structural cardiac disease. The heart shows a left ventricle with a large area of apical thinning composed of fibrotic scar tissue. The mid and basal left ventricular segments show normal myocardial thickness. The coronary arteries show no evidence of obstructive atherosclerosis. The right ventricle appears normal in size. No apparent valve damage is present. Dilation and wall-thickening of the esophagus is also noted. Which of the following factors in this patient’s medical history would be most helpful in determining the cause of death?
CorrectIncorrect
