Time limit: 0
Quiz Summary
0 of 23 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Quiz complete. Results are being recorded.
Results
0 of 23 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 23
1. Question
A 50-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after developing blurred vision and confusion. Earlier today, he was clearing and burning foliage and weeds on his property. His medical history is insignificant, and he does not take any medications. The patient has no history of illicit drug use. Temperature is 38.9 C (102 F), blood pressure is 110/76 mm Hg, pulse is 120/min, and respirations are 16/min. He is disoriented to time, place, and person. Physical examination shows flushed skin and dry oral mucosa. Both pupils are dilated and nonreactive to light and accommodation. Bowel sounds are decreased. Which of the following drugs can potentially reverse this patient’s condition?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 23
2. Question
A group of investigators is currently conducting a phase I clinical trial for a newly developed synthetic opioid that has twice the analgesic capability of morphine. After oral ingestion of a fixed dose by several volunteers, the plasma concentration of the drug is measured and determined to be subtherapeutic. Rectal administration of the same dose of the drug shows a plasma concentration well within the therapeutic range, almost double the level measured after oral intake. Which of the following best accounts for the observed difference in drug concentration following rectal administration when compared to oral administration?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 23
3. Question
A 26-year-old man with a history of excessive daytime sleepiness due to narcolepsy enrolls in a clinical trial evaluating a new stimulant medication. The patient was previously treated with modafinil, but his symptoms did not improve. It is explained to the patient that the new drug works by promoting the release of dopamine and norepinephrine from nerve terminals in the central nervous system. Adverse effects of the drug are due primarily to excess release of norepinephrine from peripheral autonomic nerve terminals. Which of the following autonomic efferents would be most affected by the use of this drug?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 23
4. Question
A 58-year-old man with type 2 diabetes mellitus comes to the emergency department with fever, malaise, lower abdominal discomfort, and left flank pain. The patient has a history of diabetic autonomic neuropathy with bladder dysfunction and has been hospitalized multiple times for recurrent urinary tract infections. His temperature is 39.4 C (103 F), blood pressure is 94/50 mm Hg, and pulse is 118/min. Height is 180 cm (5 ft 11 in), weight is 150 kg (331 lb), and BMI is 46 kg/m2. On examination, there is suprapubic and left costovertebral angle tenderness. After review of culture and sensitivity tests from his prior hospitalization, the patient is started on an empiric antibiotic regimen that includes an aminoglycoside. While calculating the appropriate dosage, the hospital pharmacy uses an adjusted body weight that is lower than the patient’s actual body weight. Which of the following best explains the use of this adjusted parameter?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 23
5. Question
A previously healthy 45-year-old male undergoes an elective hernia repair under spinal anesthesia. Postoperatively, he complains of difficulty voiding. Bladder catheterization shows a post-void residual of 300cc of urine. This patient would most likely benefit from which of the following medications?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 23
6. Question
A novel antiretroviral medication, Drug X, is being developed for treating patients with HIV infection. Initial studies show a high rate of treatment failure due to continued viral proliferation in the brain. However, treatment success rates improve when Drug X is combined with an adjuvant agent. Data comparing the two medication regimens is shown in the table below.
Drug X only Drug X + adjuvant Average cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) viral load (1 month) 1860 copies/mL 480 copies/mL Average CSF viral load (6 months) 1640 copies/mL undetectable Average serum concentration of Drug X 550 ng/ml 560 ng/ml Based on the data, the adjuvant agent most likely improves viral control through which of the following mechanisms?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 23
7. Question
A 72-year-old man comes to the office due to watery diarrhea and abdominal cramps. The symptoms began several days after he started chemotherapy for metastatic colon cancer. He denies hematochezia, melena, or bulky, foul-smelling stools. Vital signs are within normal limits, and physical examination is unremarkable. Laboratory testing reveals no electrolyte abnormalities and no leukocytosis. Stool testing is negative for infection and fecal occult blood. The patient is advised to take a medication after each loose stool. The medication works by inhibiting the release of acetylcholine in the intestinal wall but does not cross the blood-brain barrier. Which of the following is the most likely medication prescribed for this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 23
8. Question
A 24-year-old woman with a medical history of bronchial asthma comes to the office due to shortness of breath and wheezing for the past 2-3 days. She developed a cold 4 days ago and is not feeling well. The patient has a nebulizer at home and used multiple doses of albuterol with little response prior to arriving. She takes no other medications. The patient is diaphoretic and in moderate respiratory distress. Respiratory examination shows bilateral wheezing, diffusely decreased breath sounds, and increased use of accessory muscles of respiration. Laboratory results reveal a serum potassium of 3 mEq/L. Which of the following mechanisms is the most likely cause of this patient’s hypokalemia?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 23
9. Question
A researcher is conducting a retrospective study on breast cancer recurrence. Records of a number of patients with hormone receptor-positive, early-stage breast cancer who received adjuvant therapy with tamoxifen were evaluated. Various clinical, demographic, and drug concentration data were analyzed. A comparison of patients who had disease recurrence with those who remained cancer free showed that some of the relapsed patients had lower serum concentrations of endoxifen and 4-hydroxytamoxifen, the active metabolites of tamoxifen. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the drug’s ineffectiveness in this subset of patients?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 23
10. Question
A 34-year-old woman comes to the office due to inability to lose weight despite diet and exercise. She reports that she gained a significant amount of weight after she stopped smoking 4 years ago. The patient has tried several commercial weight-loss diet programs in the last year without success. She wants to lose at least 4.5 kg (10 lb) over the next few months before she gets married. The patient does not have any other medical conditions and takes no medications. Blood pressure is 122/80 mm Hg and pulse is 78/min. BMI is 33 kg/m2. Physical examination shows an obese habitus but is otherwise unremarkable. Laboratory testing for secondary causes of weight gain is unrevealing. In addition to encouraging continued efforts at lifestyle change, the physician prescribes a short course of oral phentermine for weight loss. The weight loss induced by this medication is caused by which of the following mechanisms?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 23
11. Question
A 40-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department due to difficulty breathing and muscle weakness. She was one of several people who developed symptoms in a movie theater. Temperature is 36.7 C (98.1 F), blood pressure is 112/62 mm Hg, pulse is 51/min, and respirations are 24/min. On physical examination, the patient is diaphoretic. The pupils are pinpoint and unreactive, and significant tearing is noted. Diffuse rhonchi and wheezing are present in the lungs bilaterally. Muscle strength is diminished throughout, and fasciculations are noted in the extremities. First-line therapy is administered, but the patient remains weak. Treatment with which of the following is most likely to improve this patient’s current condition?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 23
12. Question
An 85-year-old man is transferred to the hospital from a nursing home due to fever and confusion. On arrival, the patient is admitted directly to the intensive care unit with a presumptive diagnosis of septic shock. Antibiotic therapy is initiated. The patient is unable to provide any history, but his caretakers state that he has had nonspecific symptoms, including fever, for the past few days. The patient has a history of cardiovascular disease, diverticulitis, and dementia. Blood pressure is 60/40 mm Hg despite aggressive intravenous hydration. Intravenous norepinephrine is administered in response to the patient’s hypotension. Which of the following cellular changes is most likely to occur in direct response to the medication?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 23
13. Question
A 44-year-old woman comes to the office for a follow-up appointment. Six months earlier, the patient was diagnosed with essential hypertension; she has followed dietary and exercise recommendations since then. At a follow-up visit 3 months ago, she reported episodic headaches due to migraines. Her blood pressure at that visit was 145/92 mm Hg. Antihypertensive therapy with a beta blocker was started due to its beneficial effect on migraine prophylaxis. Now, 3 months later, the patient’s blood pressure has decreased to 120/80 mm Hg. She is compliant with her medication and has had no serious adverse effects. Which of the following is the most likely combination of changes in response to this patient’s treatment (AT = Angiotensin)?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 23
14. Question
A 57-year-old male with suspected bacterial pneumonia is admitted to the hospital and given ceftriaxone and azithromycin for treatment. Soon after the first dose of ceftriaxone, he complains of difficulty breathing, abdominal cramps, and lightheadedness. His current blood pressure is 70/50 mmHg, while his heart rate is 120/min. Physical examination reveals a diffuse maculopapular rash. Which of the following drugs should be administered next to this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 23
15. Question
A 75-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after a syncopal episode at his assisted living facility. The event occurred an hour ago, when he was eating lunch with other residents of the facility. The patient suddenly slumped over onto the table and awakened spontaneously after about 30 seconds. He appeared pale afterwards but was not confused, and fingerstick blood glucose was normal. Medical history includes hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, benign prostatic hyperplasia, and Alzheimer disease. Temperature is 37 C (98.6 F), supine and standing blood pressure is 110/68 mm Hg, and pulse is 62/min. The oropharyngeal mucosa is moist and jugular venous pressure is normal. The lungs are clear on auscultation and heart sounds are normal. The patient is hospitalized for observation and is found to have an episodic bradyarrhythmia and atrioventricular block. If this patient’s condition is due to a medication, which of the following is the most likely cause?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 23
16. Question
A 42-year-old man is brought to the emergency department due to nausea, vomiting, and blurred vision. He was making his own whiskey with a home moonshine still and started feeling sick after sampling the first several ounces of distillate. Funduscopic evaluation reveals optic disc hyperemia. Laboratory results show a high anion gap metabolic acidosis. It is determined that the patient’s symptoms are due to enzymatic conversion of methanol into formate by alcohol dehydrogenase. He is started on fomepizole, a medication that transiently binds to alcohol dehydrogenase and prevents methanol from accessing the enzyme’s active site. Which of the following graphs most accurately portrays the change in enzyme kinetics after administration of the antidote?
(Black curves = before treatment)
A.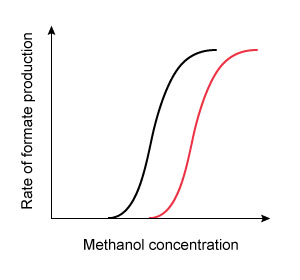 B.
B.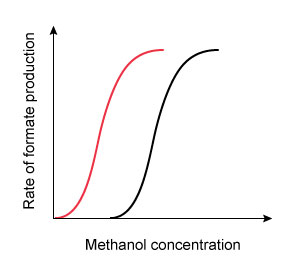 C.
C.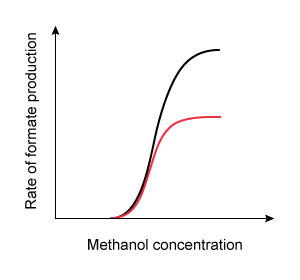 D.
D.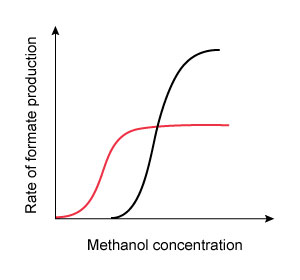 E.
E.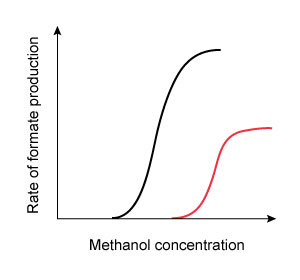 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 23
17. Question
A pharmaceutical company in the final stages of designing a new nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent develops 2 different oral formulations of the drug. Two groups of volunteers are each administered a different formulation, and average plasma drug levels are monitored over the next 12 hours. The results are shown below:

Compared to the red curve, the formulation represented by the blue curve is most likely to have which of the following characteristics?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 18 of 23
18. Question
A 57‐year‐old man is brought to the emergency department due to lethargy and altered mental status. His family suspects a suicide attempt. Medical history is significant for dilated cardiomyopathy and major depressive disorder. On arrival, blood pressure is 76/46 mm Hg, pulse is 38/min, and respirations are 16/min. Pupils are 3 mm and reactive. Oropharynx is normal. Examination shows bilateral wheezing. There is no peripheral edema. Capillary refill is 3 seconds. There is no diaphoresis. Which of the following categories of medication did this patient most likely ingest?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 23
19. Question
An 82-year-old woman is brought to the office for a new patient evaluation. She recently moved in with her daughter. The patient reports frequent dizziness but cannot provide additional details regarding her symptoms. Medical history includes moderate dementia, hypertension, transient ischemic attack, depression, and chronic insomnia. Blood pressure is 124/72 mm Hg, and pulse is 66/min and regular. Neurologic examination shows disorientation to time and place but normal deep tendon reflexes and no focal sensory or motor deficits. The patient’s medication schedule includes 12 different drugs that are used to manage her chronic conditions. Which of the following medications should be discontinued at this time?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 23
20. Question
A 78-year-old woman is admitted to the hospital due to altered mental status. Medical history is significant for pyelonephritis, type 2 diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, and heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Temperature is 36.2 C (97.2 F), blood pressure is 80/50 mm Hg, pulse is 120/min, and respirations are 24/min. Oxygen saturation is 90% on room air. Examination shows bilateral crackles. After she is started on appropriate treatment, including initiation of norepinephrine infusion, her blood pressure increases and her heart rate slightly decreases. This patient’s change in heart rate is most likely due to norepinephrine’s effect on which of the following receptors?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 21 of 23
21. Question
A 65-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to substernal chest discomfort and intermittent palpitations that began this morning. The patient has a history of coronary artery disease and stable angina that is managed medically. He takes high-dose metoprolol, atorvastatin, and low-dose aspirin. The patient reports that he has been traveling for the past week and ran out of his medications 2 days ago. Temperature is 37 C (98.6 F), blood pressure is 148/82 mm Hg, and pulse is 112/min. ECG reveals sinus tachycardia with a 1-mm ST segment depression in the lateral leads. Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient’s presentation?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 22 of 23
22. Question
A 44-year-old previously healthy woman comes to the emergency department due to a 2-day history of left flank pain, dysuria, fever, and chills. Temperature is 38.9 C (102 F), blood pressure is 80/40 mm Hg, and pulse is 140/min and regular. Physical examination shows left costovertebral angle tenderness. Laboratory studies reveal leukocytosis, pyuria, and bacteriuria. Empiric broad-spectrum antibiotics and intravenous fluids are administered. The patient remains persistently hypotensive, and an intravenous phenylephrine infusion is begun. Several minutes later, her heart rate decreases to 100/min. Compared to just prior to the infusion, which of the following intracellular changes are expected in this patient?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 23 of 23
23. Question
A 6-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department by her parents after they found her unresponsive in the basement. They report that her younger sister sprayed the patient with a bottle that had been filled with pesticide to help rid the house of insects. Temperature is 36.6 C (98 F), blood pressure is 110/60 mm Hg, pulse is 58/min, and respirations are 42/min. On examination, the patient is lethargic and salivating. Which of the following medications should be administered first during treatment of this patient’s current condition?
CorrectIncorrect
