Time limit: 0
Quiz Summary
0 of 21 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Quiz complete. Results are being recorded.
Results
0 of 21 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 21
1. Question
A 35-year-old woman comes to the office for evaluation of fatigue and exertional dyspnea. She has a history of systemic lupus erythematosus and is noncompliant with therapy. The patient takes naproxen as needed for joint pains. Vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows mild pallor. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory results are as follows:
Hemoglobin
8.6 g/dL
Mean corpuscular volume
80 mm3
Creatinine
0.8 mg/dL
Iron, serum
40 µg/dL
Total iron-binding capacity
180 µg/dL
(normal: 250-460 µg/dL)
Lactate dehydrogenase
72 U/L
Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of her current condition?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 21
2. Question
A 45-year-old man comes to the office due to 3 months of exertional fatigue and weight loss. He is sexually active with multiple male partners. Temperature is 37.9 C (100.2 F), blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, pulse is 84/min, and respirations are 13/min. BMI is 20 kg/m2. The patient appears chronically ill and has mucosal pallor. There are thick, white plaques over the buccal mucosa and soft palate. Anterior and posterior cervical lymphadenopathy is present. The lungs are clear to auscultation. The abdomen is soft and nontender. There is no organomegaly. Laboratory results are as follows:
Hematocrit
28%
Mean corpuscular volume
76 µm3
Platelets
160,000/mm3
Leukocytes
4,100/mm3
Iron, serum
30 µg/dL
Total iron-binding capacity
190 µg/dL
(normal: 250-460)
Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient’s anemia?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 21
3. Question
A 6-month-old boy is brought to the clinic for a wellness visit. The mother states he has been doing well since his last visit and has had no recent illnesses. The patient was born at term and has no chronic medical conditions. He takes no medications aside from vitamin D supplementation. The patient had been exclusively breastfed. The mother recently began introducing pureed fruits and vegetables. The patient continues to breastfeed but does not consume iron-fortified cereal. Vital signs are normal. The anterior fontanelle is open and flat. The oropharynx is clear. The neck is supple, and cardiopulmonary examination is unremarkable. The abdomen is soft with no organomegaly. It is explained to the mother that the patient is at risk for developing iron deficiency anemia. If no dietary changes are made, which of the following laboratory values is most likely to decrease first in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 21
4. Question
A 61-year-old woman is sent to the emergency department by her oncologist due to possible systemic infection from an indwelling venous catheter. The patient was recently diagnosed with breast adenocarcinoma and had a central venous catheter placed to receive systemic chemotherapy. She completed a cycle of cytotoxic chemotherapy 10 days ago. The patient has no other medical conditions. Laboratory studies performed at the office revealed a leukocyte count of 800/mm3 with 10% neutrophils. Which of the following signs typically associated with a catheter-related bloodstream infection is most likely to be absent in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 21
5. Question
A 14-year-old girl with sickle cell disease is admitted to the hospital due to fever for 2 days. Temperature is 38 C (100.4 F), blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, pulse is 120/min, and respirations are 18/min. Examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies reveal:
Complete blood count
Hemoglobin
10 g/dL
Mean corpuscular volume
86 µm3
Reticulocytes
2%
Platelets
240,000/mm3
Leukocytes
14,000/mm3
Blood cultures are obtained, and appropriate pharmacotherapy is initiated. Her peripheral blood smear is shown in the exhibit. The smear findings indicated by the arrow most likely reflect which of the following processes?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 21
6. Question
An 18-year-old woman collapsed while practicing for a marathon in hot, humid weather. The patient subsequently vomited 3 times and had a tonic-clonic seizure. She has no chronic medical conditions and takes no medications. The patient does not use alcohol or illicit drugs. Temperature is 40.8 C (105.4 F), blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg, pulse is 130/min, and respirations are 22/min. The patient is profusely sweating and is confused. Pupils are sluggishly reactive to light. Cardiopulmonary examination reveals clear lungs and normal heart sounds. Laboratory results are as follows:
Complete blood count
Hemoglobin
15.8 g/dL
Platelets
90,000/mm3
Leukocytes
10,000/mm3
Coagulation studies
PT
20 sec
Activated PTT
43 sec
Which of the following sets of hematologic findings is most likely to be present in this patient?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 21
7. Question
A 66-year-old woman comes to the office due to 2 months of worsening fatigue and dyspnea with moderate exertion. The patient has a history of breast cancer treated with surgery and combination chemotherapy 6 years ago. She has no other medical conditions. Vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination reveals normal jugular venous pressure, clear lungs, and normal heart sounds; there is no hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, or extremity edema. Laboratory results are as follows:
Hemoglobin
7.2 g/dL
Mean corpuscular volume
108 µm3
Reticulocytes
1%
Platelets
90,000/mm3
Leukocytes
3,800/mm3
Peripheral blood smear shows oval macrocytic red cells and hyposegmented neutrophils. Bone marrow biopsy of this patient is most likely to reveal which of the following?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 21
8. Question
A 22-year-old woman comes to the office due to worsening dyspnea and heart pounding with exercise for the last week. She has no chronic medical conditions but reports aches and pains over the past several weeks. The patient takes ibuprofen as needed but no other medications. Temperature is 37.2 C (99 F), blood pressure is 138/86 mm Hg, and pulse is 90/min. BMI is 18 kg/m2. Physical examination shows an erythematous rash in sun-exposed regions. The lungs are clear to auscultation. A midsystolic click and systolic murmur are heard best at the apex without radiation. There is mild tenderness of joints. Laboratory results are as follows:
Hemoglobin
7.8 g/dL
Reticulocytes
6%
Platelets
205,000/mm3
Leukocytes
11,200/mm3
Creatinine
1.4 mg/dL
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s hematologic findings?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 21
9. Question
A 53-year-old woman comes to the office due to progressive distension and tightness in her right lower extremity for the past year. She has had no shortness of breath, fever, or skin rash. The patient was diagnosed with melanoma of the right thigh approximately 2 years ago and underwent surgical resection. Two of her inguinal lymph nodes tested positive for metastasis, and she subsequently underwent inguinal lymphadenectomy and received adjuvant therapy. Recent imaging revealed no evidence of recurrent malignancy. The patient’s medical history also includes hypertension and hyperlipidemia. Vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows clear lungs and normal heart sounds without murmurs or gallops. No jugular venous distension is present. The right lower extremity is significantly larger in diameter than the left. Edema is present up to the thigh, with mild skin indentation after application of pressure. The skin overlying the involved area is thickened and dry. Laboratory testing, including complete blood count, serum metabolic panel, and urinalysis, is within normal limits. Treatment of this patient’s symptoms should include which of the following strategies?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 21
10. Question
A 25-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department after a motor vehicle collision. She has a pneumothorax, multiple rib fractures, and a right femur and tibial fracture. A chest tube is placed. The patient receives resuscitation and undergoes repair of the femur and tibial fractures. The following day, she develops respiratory distress, decreased urine output, and persistent bleeding from the chest tube drains and around the intravenous lines. Which of the following sets of laboratory findings is most likely to be seen in this patient?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 21
11. Question
A 66-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to abdominal cramps and watery diarrhea for the past day. The patient was hospitalized 2 weeks ago due to acute pyelonephritis and was treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics. She has a remote history of Hodgkin disease treated with chemotherapy and radiation treatment but no other chronic medical conditions. The patient’s only home medication is a multivitamin supplement. Temperature is 38.3 C (100.9 F), blood pressure is 124/72 mm Hg, and pulse is 92/min. There is mild generalized abdominal tenderness with no guarding or rebound. The remainder of the physical examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory results are as follows:
Hemoglobin
12.8 g/dL
Platelets
380,000/mm3
Leukocytes
32,000/mm3
Neutrophils
80%
Bands
8%
Metamyelocytes
2%
Lymphocytes
10%
Prior blood cell count at the time of hospital discharge was normal. Stool testing for Clostridioides difficile is positive. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient’s leukocytosis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 21
12. Question
A 68-year-old man comes to the office to establish care. He has type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated by chronic kidney disease and peripheral sensory neuropathy. Medical history is notable for hypertension and coronary artery disease. The patient works for an agricultural supply company and spends most of his day walking and standing on a warehouse floor. Vital signs are normal. BMI is 34 kg/m2. Examination of the lower extremities shows decreased sensation to monofilament testing below the knees bilaterally, with 2+ pitting edema, varicosities, and extensive skin discoloration, as shown below.

Which of the following is the most likely cause of the discoloration in this patient’s skin?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 21
13. Question
A 29-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to fever and headache for the last week. The patient has a generalized tonic-clonic seizure while being evaluated. Laboratory results are as follows:
Hemoglobin
6.1 g/dL
Platelets
16,000/mm3
Creatinine
2.2 mg/dL
Total bilirubin
4.3 mg/dL
Serum haptoglobin
undetectable
PT
11 sec (INR 1.1)
Activated PTT
30 sec
Peripheral blood smear is shown in the exhibit. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient’s current condition?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 21
14. Question
A 60-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to 10 days of worsening cough, shortness of breath, and right-sided chest pain. The patient also has had low-grade fever, fatigue, and unspecified weight loss. A month ago, he was hospitalized for 2 days due to right lower lobe pneumonia. Although oral antibiotics were prescribed at discharge, he did not get the prescription filled because his symptoms had improved. Temperature is 38.2 C (100.8 F), blood pressure is 116/70 mm Hg, pulse is 104/min, and respirations are 18/min. Physical examination is notable for decreased breath sounds at the right lung base. Chest imaging reveals loculated pleural fluid on the right side. Laboratory analysis reveals the following:
Hemoglobin
10.4 g/dL
Mean corpuscular volume
96 µm3
Platelets
580,000/mm3
Leukocytes
17,200/mm3
(80% neutrophils)
Blood cell counts were normal a month ago at the time of hospital discharge. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient’s increased platelet count?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 21
15. Question
A 15-month-old boy is brought to the clinic for evaluation of recurrent mouth ulcers. Over the past 5 months, his mother has noted that he has had periodic episodes of mouth pain and oral ulcers. She says the episodes usually last for a couple of days and then resolve without intervention. The boy has no known medical conditions and takes no medications. Vital signs are normal. Examination shows mucositis. The rest of the examination is unremarkable. Complete blood count (CBC) reveals an absolute neutrophil count of 390/mm3. Hemoglobin level and platelet count are normal. Serial CBC results are documented over the next 6 weeks, revealing the pattern shown below:
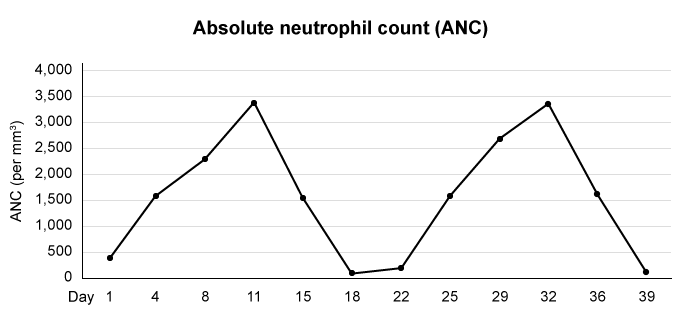
The patient returns to the clinic on Day 39. Examination of this patient’s bone marrow would most likely reveal an abnormal increase in which of the following?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 21
16. Question
A 3-year-old boy diagnosed with thalassemia major receives multiple transfusions to maintain his blood hemoglobin level. On physical examination, his liver and spleen are mildly enlarged. He also has glucose intolerance as demonstrated by an oral glucose tolerance test. Which of the following therapies would prevent congestive cardiac failure in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 21
17. Question
A 32-year-old woman comes to the office due to bloating, intermittent diarrhea, and abdominal cramps. Symptoms have been ongoing for many years and are usually triggered by meals. Past medical history and family history are otherwise unremarkable. Vital signs are within normal limits. BMI is 27 kg/m2. The patient is well-appearing, and the abdomen is soft and nontender. Laboratory analysis is unremarkable. The patient is diagnosed with irritable bowel syndrome, and it is recommended that she take loperamide and consume an adequate amount of dietary fiber. After reading about her disorder on the internet, the patient decides to manage her symptoms with a strict vegan diet that includes a vitamin B12 supplement. This patient is at highest risk for dietary deficiency of which of the following nutrients?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 18 of 21
18. Question
A 16-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department due to nosebleeds and worsening bruising. He first noticed mild bruising on his lower legs a couple of days ago, and since then, the bruises have progressed along the thighs and hips. Today, he developed epistaxis that was difficult to control with applied pressure. The patient has Crohn disease and has had multiple hospitalizations for complications. He takes no anticoagulants. Vital signs are normal. Scant blood oozes from the nares. Abdominal examination is unremarkable, and pulses are strong. Skin examination shows large ecchymoses distributed along the lower extremities. Laboratory results are as follows:
Platelets
230,000/mm3
PT
28 sec
Activated PTT
68 sec
Reversal of this patient’s coagulation abnormalities is achieved with the intravenous administration of a medication. This treatment most likely directly affected which of the following cellular processes?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 21
19. Question
A 5-year-old boy is brought to the office by his parents to establish medical care. The family recently immigrated to the United States from Nigeria. Both parents have sickle cell trait, and the patient was diagnosed with homozygous sickle cell disease (HbSS) at the age of 6 months. He has had several prior vasoocclusive crises and takes folic acid and hydroxyurea. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Hemoglobin electrophoresis in this patient is most likely to reveal which of the following predominant hemoglobin patterns?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 21
20. Question
A 55-year-old man comes to the office due to several months of progressive fatigue. He does not have chest pain or shortness of breath. Medical history is significant for hypertension and obesity. BMI is 45 kg/m2. Examination shows mild mucosal pallor. Laboratory results are as follows:
Complete blood count
Hemoglobin
8.6 g/dL
Mean corpuscular volume
84 µm3
Reticulocytes
0.2%
Platelets
200,000/mm3
Leukocytes
7,500/mm3
Serum chemistry
Blood urea nitrogen
14 mg/dL
Creatinine
0.8 mg/dL
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s anemia?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 21 of 21
21. Question
A 65-year-old man comes to the office due to a few weeks of progressive exertional dyspnea and fatigue. He has had no chest pain, fever, or cough. The patient has a history of mild aortic stenosis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, obesity, hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia. Temperature is 36.7 C (98 F), blood pressure is 130/78 mm Hg, pulse is 82/min, and respirations are 16/min. BMI is 28 kg/m2. Pulse oximetry shows 96% on room air. Mucosal pallor is present, but there is no jaundice, lymphadenopathy, or jugular venous distension. Cardiopulmonary examination reveals a 2/6 systolic ejection murmur at the second right intercostal area. The abdomen is soft and nontender; there is no palpable hepatosplenomegaly. Peripheral pulses are normal. Laboratory results are as follows:
Complete blood count
Hemoglobin
7.8 g/dL
Platelets
98,000/mm3
Leukocytes
3,800/mm3
Peripheral blood smear is shown below:

Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient’s current condition?
CorrectIncorrect
