Quiz Summary
0 of 40 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 40 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- NBME 7 BLOCK 4 0%
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 40
1. Question
A 64-year-old man comes to the office for follow-up of hypertension. At the last 2 visits, his blood pressure was persistently elevated. The patient has been treated with lisinopril for the past 5 years, but his other blood pressure medications have been changed several times due to various adverse effects. Medical history is significant for type 2 diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease with stable angina, and moderately increased albuminuria. Blood pressure is 145/87 mm Hg and pulse is 70/min. BMI is 31 kg/m2. Physical examination shows trace bilateral lower extremity edema. ECG is unremarkable. Serum laboratory results are as follows:
Sodium
138 mEq/L
Potassium
5.3 mEq/L
Chloride
104 mEq/L
Bicarbonate
24 mEq/L
Calcium
9.5 mg/dL
Creatinine
1.0 mg/dL
Review of the patient’s medical records shows similar serum laboratory results 6 months ago. Which of the following medications should be avoided in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 40
2. Question
A 71-year-old woman comes to the office for follow-up. She has a history of systolic heart failure and was hospitalized 2 weeks ago for an exacerbation, which was treated with intravenous diuretics. Since discharge the patient has been taking oral diuretics and says her shortness of breath has improved, but she is now experiencing muscle weakness and cramping. Blood pressure is 128/72 mm Hg and pulse is 80/min. Physical examination shows mildly decreased muscle strength in the lower extremities. Laboratory evaluation reveals a serum potassium level of 2.2 mEq/L. The patient receives potassium supplements, which improve the weakness. Another diuretic is added to her medical regimen to help prevent this adverse effect in the future. This additional medication predominantly acts on which of the following nephron segments?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 40
3. Question
A 67-year-old man with nonischemic cardiomyopathy comes to the office for follow-up. He recently was hospitalized for acute decompensated heart failure. The patient’s symptoms have improved with multidrug treatment, but he has persistent shortness of breath on mild exertion. He has a history of hypertension and hypercholesterolemia. Blood pressure is 115/70 mm Hg and pulse is 66/min. There is a third heart sound on heart auscultation and mild lower extremity pitting edema. A recent echocardiogram showed a left ventricular ejection fraction of 30%. Which of the following diuretics would most likely improve survival if added to this patient’s current regimen?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 40
4. Question
A 56-year-old woman comes to the emergency department with facial swelling and difficulty breathing. She woke up today with a “feeling of fullness” in her lips, and 2 hours later her husband said that her lips looked puffy. There is no itching or skin rash. The patient has had no similar symptoms before. She has a history of gastroesophageal reflux disease and takes lansoprazole daily. She also began taking lisinopril 2 months ago for hypertension. The patient’s blood pressure is 135/75 mm Hg. On examination, there is moderate swelling of her lips and tongue. Mild audible stridor without wheezing is present. Which of the following is the most likely mechanism responsible for this patient’s symptoms?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 40
5. Question
A 60-year-old man comes to the office for a routine follow-up visit. He feels well overall except for an intermittent, mild, generalized headache. The patient has no known medical problems and takes no medications. He does not smoke, follows a generally healthy diet, and exercises daily. On examination, his blood pressure is 150/85 mm Hg, and he is started on lisinopril. At a follow-up visit, the patient’s blood pressure is 128/78 mm Hg. He also has a dry cough that began a few weeks after starting lisinopril. This drug is stopped and losartan is now prescribed. The patient seems to be compliant with his medication; the cough resolves and he experiences no significant side effects. When compared with no treatment at all, this patient’s current therapy is most likely to result in which of the following changes?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 40
6. Question
A 43-year-old man comes to the office due to swelling of the legs and abdomen. The patient has a history of alcohol-induced cirrhosis, and his ascites had been well controlled with furosemide. Over the past week, he has had increasing bilateral lower extremity and abdominal swelling despite taking a diuretic as prescribed. The patient reports no change in dietary sodium or water intake but states he has been taking over-the-counter ibuprofen after injuring his back recently. He stopped drinking alcohol 2 years ago and does not use tobacco or illicit drugs. Physical examination shows 3+ bilateral lower extremity edema and moderate ascites. Which of the following changes most likely contributed to the acute deterioration in this patient’s condition?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 40
7. Question
A 12-year-old girl is being evaluated for recurrent episodes of self-limited colicky abdominal pain and nausea lasting several days. She was also recently hospitalized for an episode of difficulty breathing. The patient has no significant past medical history, but her mother has a history of attacks of severe abdominal pain and diarrhea. Physical examination is unremarkable. Laboratory evaluation reveals decreased serum complement C4 and C1 esterase inhibitor levels. Which of the following drugs is contraindicated in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 40
8. Question
A 55-year-old man comes to the office for follow-up of abnormal serum chemistries found on routine laboratory testing. He has a history of hypertension, for which he is being treated with pharmacologic therapy, weight loss, and dietary salt restriction. Blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg and pulse is 80/min. BMI is 27 kg/m2. Physical examination reveals no abnormalities. Laboratory studies are as follows:
Serum chemistry
Sodium
134 mEq/L
Potassium
3.8 mEq/L
Blood urea nitrogen
18 mg/dL
Creatinine
0.8 mg/dL
Calcium
11.0 mg/dL
Glucose
98 mg/dL
Albumin
4 g/dL
Parathyroid hormone
decreased
Which of the following is most likely responsible for these findings?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 40
9. Question
A 56-year-old man comes to the emergency department with acute onset of severe right foot pain. The pain is associated with local redness and swelling, but he has had no fever or recent trauma. The patient has never had similar symptoms. Medical history is significant for type 2 diabetes mellitus, mixed hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and coronary artery disease, for which he takes several medications. Physical examination shows a swollen, tender first metatarsophalangeal joint. Aspiration reveals a high leukocyte count, negative Gram stain, and numerous needle-shaped negatively birefringent crystals. Which of the following drugs is most likely to have precipitated this patient’s condition?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 40
10. Question
A 27-year-old nursing assistant with a history of major depression and bulimia is brought to the emergency department after a suicide attempt. She claims to have ingested several diuretic pills 18 hours ago. The patient complains of frequent, large-volume urinations that started shortly after she ingested the pills. She has also been very thirsty but she denies nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. Her temperature is 36.7 C (98 F), blood pressure is 96/60 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 14/min. Physical examination shows dry oral mucosa and reduced skin turgor. Laboratory results are as follows:
Serum chemistry Sodium 122 mEq/L Potassium 2.8 mEq/L Chloride 84 mEq/L Bicarbonate 28 mEq/L Blood urea nitrogen 22 mg/dL Creatinine 1.4 mg/dL Calcium 11.4 mg/dL Albumin 3.9 g/dL Which of the following medications did this patient most likely ingest?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 40
11. Question
A 65-year-old man comes to the office for follow-up monitoring of type 2 diabetes mellitus. He was diagnosed with diabetes 7 years ago and follows a strict diet to control his blood sugar level. The patient takes no medications. Blood pressure is 139/88 mm Hg and pulse is 70/min. Physical examination shows decreased lower-extremity sensation with a 10-g monofilament. His most recent hemoglobin A1c is 7.4% (normal, <5.6%). Serum creatinine is 1.0 mg/dL and serum potassium is 3.8 mEq/L. Further laboratory evaluation reveals increased urinary albumin excretion, but a conventional urinalysis is within normal limits. In addition to starting antihyperglycemic treatment, which of the following is the best pharmacotherapy for this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 40
12. Question
An unresponsive 62-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after sustaining multiple injuries in a major motor vehicle accident. He is obtunded but responds to painful stimuli. His blood pressure is 160/90 mm Hg, pulse is 72/min, and respirations are 10/min. A few hours after initial treatment and stabilization, he develops severe tachypnea and decreased oxygenation. His chest x-ray shows evidence of pulmonary edema. He is rapidly intubated and given oxygen but acutely worsens and dies a few hours later, despite aggressive measures. Which of the following drugs could have caused this patient’s condition?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 40
13. Question
A 72-year-old woman presents with difficulty hearing. She was admitted 1 week ago for dyspnea, orthopnea, and bilateral leg swelling which has been slowly improving with treatment. Her family members report that for the past 2 days, she has been turning her TV volume higher and they have to speak loudly for her to hear. Her hearing was normal prior to the hospitalization. Her medical problems include hypertension, heart failure, and chronic kidney disease. Examination shows moderate bilateral sensorineural hearing loss. Which of the following medications most likely contributed to this patient’s hearing impairment?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 40
14. Question
A 70-year-old man comes to the office due to increasing headaches, nausea, and vomiting. The patient has never had these symptoms before. Medical history is significant for a transient ischemic attack that led to a right carotid endarterectomy 5 years ago. He has no other medical conditions, and his only medications are aspirin and atorvastatin. The patient smoked a pack of cigarettes a day for 20 years but quit 20 years ago. Blood pressure is 220/120 mm Hg and pulse is 70/min. Neurologic examination shows no focal lesions. Bilateral abdominal bruits are present. Blood testing in this patient would most likely show which of the following?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 40
15. Question
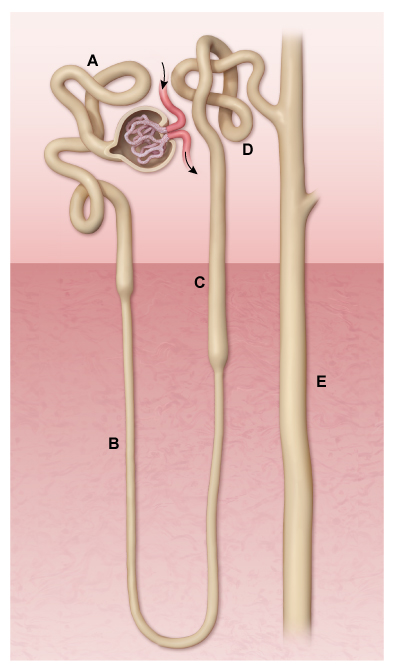
A 64-year-old man comes to the office after learning at the dentist’s office that he has elevated blood pressure. The patient is a combat veteran and has always been “fit as a bull.” He has undergone various minor surgical procedures for wartime injuries. He reports many years of tobacco and alcohol use but currently uses neither. On careful questioning, he describes chest pain on exertion. Blood pressure is 155/90 mm Hg and pulse is 76/min. Physical examination is significant for decreased pulse amplitude over the right femoral artery and a systolic bruit over the left carotid artery. Resting ECG is unremarkable, and serum creatinine is 1.1 mg/dL. Urinalysis is negative for protein. Treatment for hypertension is initiated with ramipril. On a follow-up visit 3 weeks later, blood pressure is 142/85 mm Hg but serum creatinine has increased to 2 mg/dL. This laboratory finding is best explained by an effect of the drug on which of the following structures (as indicated in the image)?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 40
16. Question
A 63-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to muscle weakness with severe cramping in the lower extremities. The cramps are severe enough to disrupt his sleep. The patient also exercises daily but has had to suspend his exercise regimen in the last 3 days due to the symptoms. Past medical history is notable for hypertension, for which he was started on chlorthalidone and amlodipine 4 weeks ago. Blood pressure in the emergency department is 140/86 mm Hg and pulse is 90/min. The heart has a regular rate and rhythm, and he has palpable pedal pulses with no peripheral edema. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s muscular symptoms?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 40
17. Question
A 36-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to severe, acute knee pain that awoke him from sleep. He has a history of end-stage renal disease for which he underwent a renal transplant 8 weeks ago. The patient takes an immunosuppressive regimen that includes cyclosporine and low-dose prednisone. He visited his nephrologist last week and serum creatinine levels were normal with no proteinuria. Temperature is 37.5 C (99.5 F), blood pressure is 136/78 mm Hg, and pulse is 88/min. Examination shows redness, warmth, and a small effusion in the left knee. Passive range of motion at the knee causes severe pain. Microscopic examination of joint fluid from the knee shows numerous neutrophils as well as both intra- and extracellular crystals as shown in the exhibit. Which of the following mechanisms is most likely responsible for this patient’s acute symptoms?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 18 of 40
18. Question
A 62-year-old man is brought to the emergency department with a 1-hour history of sudden-onset severe headache and progressive lethargy. Medical history is significant for hypertension. Temperature is 37 C (98.6 F), blood pressure is 180/95 mm Hg, pulse is 60/min, and respirations are 10/min. On physical examination, the patient responds to painful stimuli only but does not move his left extremities to pain. The right pupil is larger than the left and is sluggish to react. CT scan of the head shows right basal ganglia hemorrhage causing compression of the right lateral ventricle and shift of the midline structures. Blood cell counts, serum chemistry studies, and coagulation profile are within normal limits. Endotracheal intubation is performed for airway protection, and an intravenous bolus of mannitol is administered. Which of the following is the most likely acute effect of the medication given to this patient?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 40
19. Question
A 75-year-old man comes to the office for follow-up of hypertension. In recent weeks, his blood pressure has consistently been 160-165/85-90 mm Hg. Medical history includes a right carotid endarterectomy for recurrent transient ischemic attacks, a myocardial infarction 2 years ago, and coronary artery bypass surgery for unstable angina 1 year ago. The patient currently takes metoprolol, clopidogrel, amlodipine, and rosuvastatin. He quit smoking 20 years ago and does not drink alcohol. The patient is compliant with his medical therapy and office visits. Ramipril is added to his medication regimen. One week later, creatinine is 2.1 mg/dL, up from a baseline of 1.1 mg/dL. Assuming the patient’s baseline urinalysis is normal, a repeat urinalysis at this time would most likely reveal which of the following?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 40
20. Question
A 70-year-old man comes to the office for follow-up of hypertension. He has been taking amlodipine but his recent home blood pressure readings have been elevated. The patient has a long smoking history and, despite many attempts at quitting, continues to smoke cigarettes. Blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg and pulse is 76/min. Examination shows a bruit on auscultation of the abdomen. Further evaluation reveals bilateral renal artery stenosis. After initial discussion, the patient is started on daily lisinopril therapy. The patient is advised to return to the clinic in a few days. The close follow-up is recommended due to which of the following anticipated effects in this patient’s kidney function?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 21 of 40
21. Question
A 62-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up appointment. He experienced acute myocardial infarction 2 years ago and has a long history of hypertension. After physical examination and laboratory testing, the physician decides to increase the dose of his diuretic. Repeat laboratory studies indicate that his serum calcium level increases after this adjustment. The diuretic used in this patient acts predominantly on which of the following nephron segments?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 22 of 40
22. Question
A 62-year-old man comes to the emergency department with severe shortness of breath and orthopnea. His medical history is significant for long-standing hypertension and myocardial infarction a year ago. Physical examination reveals elevated jugular venous pressure, crackles on lung auscultation, and pitting edema of the lower extremities. The patient is given a medication and experiences brisk diuresis with significant symptom relief. The drug most likely used to treat this patient’s condition predominantly acts on which of the following nephron segments?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 23 of 40
23. Question
An 80-year-old woman presents to the office for evaluation of progressively worsening urinary incontinence. The patient reports that she is leaking urine “all of the time” and is using the bathroom multiple times at night. She loses urine immediately after she has the urge to void and often cannot make it to the bathroom. The patient was recently diagnosed with mild cognitive impairment but maintains independence with the assistance of her husband. She has no other medical problems. Vital signs are normal. Pelvic examination shows vaginal atrophy but is otherwise normal. There is no leaking of urine with cough or Valsalva maneuver. Postvoid residual volume and urinalysis are normal. A medication with which of the following pharmacodynamic effects would be most helpful in treating this patient’s urinary incontinence?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 24 of 40
24. Question
A 54-year-old man is hospitalized after a planned abdominal surgery. One of his physicians administers a new drug whose mechanism of action you do not know. Shortly after administration of the drug the patient develops flushing, diaphoresis and nausea. His blood pressure is 100/70 mmHg and heart rate is 55/min. His pupils are constricted but reactive to light. This medication is most likely given for which of the following conditions?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 25 of 40
25. Question
A 52-year-old woman comes to the office due to episodic incontinence for the last several months. She states that these episodes occur almost every day and are very embarrassing. They begin as an urge to urinate, and most of the time she cannot make it to the bathroom before urinating on herself. Physical examination, including pelvic examination, is unremarkable. A urinalysis is within normal limits. Urodynamic evaluation is significant for detrusor instability. Initial non-pharmacologic measures are unsuccessful and pharmacologic therapy is considered. The appropriate treatment for this patient’s condition includes an agent with which of the following effects?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 26 of 40
26. Question
A 56-year-old woman comes to clinic for follow-up of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Over the last 3 months, the patient has been hospitalized twice due to acute decompensation of heart failure that required treatment with intravenous furosemide. Since her most recent discharge, she has been taking high doses of oral furosemide, but she continues to have progressive lower extremity edema and weight gain. Serum creatinine is 1.2 mg/dL and serum potassium is 4.1 mEq/L. The patient is started on metolazone. The addition of metolazone is likely to assist in treating this patient because of which of the following effects of furosemide?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 40
27. Question
A 56-year-old man with type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease is found to have a persistently elevated serum potassium level. He takes lisinopril. Blood pressure is 130/90 mm Hg. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. The patient is prescribed patiromer therapy. Which of the following best describes the mechanism of action of this medication?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 28 of 40
28. Question
A 62-year-old man comes to the office due to decreased libido and failure to achieve satisfactory erections. The patient has coronary artery disease and heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and was prescribed spironolactone therapy several months ago. Other medications include aspirin, lisinopril, furosemide, and metoprolol. Blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg and pulse is 70/min. Oxygen saturation is 95% on room air. Examination shows a left ventricular S3 and trace pitting ankle edema. Breast examination demonstrates bilateral enlargement with mild tenderness. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s current symptoms?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 29 of 40
29. Question
A 21-year-old health care worker with a history of bulimia nervosa is brought to the hospital due to generalized weakness and dizziness. She reports no vomiting or laxative use. On admission, she is fully responsive. Blood pressure is 110/60 mm Hg and pulse is 102/min. Physical examination shows dry mucous membranes. Urine screening for diuretics reveals a large amount of furosemide. Which of the following sets of laboratory findings would most likely suggest that this patient is abusing furosemide to lose weight?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 30 of 40
30. Question
A 68-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to a 1-week history of increasing leg and abdominal swelling. The patient has a history of pulmonary hypertension and cor pulmonale from advanced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Other medical conditions include hypertension and gout. Physical examination shows scattered rhonchi, prolonged expiratory phase of expiration, mild ascites, and extensive edema of the abdominal wall and lower extremities. The patient is hospitalized and intravenous loop diuretic therapy is begun. Two days later, acetazolamide is added to his treatment regimen. Which of the following most likely prompted the additional therapy in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 31 of 40
31. Question
A 59-year-old man who is being treated for hypercholesterolemia, diabetes, and hypertension comes to the physician for a scheduled follow-up visit three weeks after starting a new medication. He has no new complaints. Blood work drawn yesterday shows an interim increase in potassium from 4.8 mEq/L to 5.2 mEq/L and a creatinine elevation from 1.2 mg/dL to 1.6 mg/dL. Administration of which of the following drugs is most likely responsible for the change in this patient’s renal function?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 32 of 40
32. Question
A 54-year-old man comes to the office due to new-onset muscle cramps. The patient has a history of hypertension and was started on hydrochlorothiazide 4 weeks ago. Blood pressure is 138/86 mm Hg and pulse is 78/min. Examination shows no abnormalities. Based on his most recent laboratory results, triamterene is added to the current therapy. Which of the following best describes the mechanism of action of this medication?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 33 of 40
33. Question
A 55-year-old woman with stage IV chronic kidney disease due to type 2 diabetes mellitus comes to the office for a follow-up visit. Blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg and pulse is 78/min. BMI is 31 kg/m2. Laboratory results are as follows:
Hemoglobin
10.5 g/dL
Calcium
8.8 mg/dL
Albumin
3.7 g/dL
Phosphorus
7.2 mg/dL
Creatinine
3.3 mg/dL
Blood urea nitrogen
88 mg/dL
Parathyroid hormone
100 pg/mL (normal: 10-65)
The patient’s serum phosphorus has been persistently elevated despite strict dietary phosphate restriction. Treatment with sevelamer is initiated. This medication reduces the serum phosphorus level by which of the following mechanisms?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 34 of 40
34. Question
A 57-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to the abrupt onset of severe right eye pain and ipsilateral headache. The patient also has severe nausea and describes seeing halos around objects. After initial treatment with the appropriate medication, the pain severity decreases. Urine output also slightly increases, and the urine pH becomes more alkaline. The medication used to treat this patient’s eye condition predominantly acts on which of the following nephron segments?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 35 of 40
35. Question
A 74-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to left hip pain and inability to walk after a fall. She is being treated by her primary care provider for various medical conditions including hypertension, congestive heart failure, chronic atrial fibrillation, type 2 diabetes mellitus, trigeminal neuralgia, depression, and gastroesophageal reflux disease. On examination, the left leg is shorter than the right and externally rotated. She is not able to move the left hip. An imaging study confirms acute femoral neck fracture. Her bone density, measured by quantitative x-ray densitometry, is consistent with osteoporosis. Which of the following drugs, had it been used as part of the medical regimen, would have had a beneficial effect on calcium homeostasis and reduced this patient’s fracture risk?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 36 of 40
36. Question
A 57-year-old man comes to the office for a follow-up appointment. He has a history of systolic heart failure, which has been managed with appropriate medical therapy. The patient experiences significant functional impairment at baseline and is able to walk only short distances. His most recent echocardiogram revealed a left ventricular ejection fraction of 30% (normal ≥55%). The physician decides to add spironolactone to the treatment regimen. The addition of this medication is most likely to cause a decrease in which of the following?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 37 of 40
37. Question
A 55-year-old woman is treated with ramipril for primary (essential) hypertension. Her blood pressure decreases to normal value over several weeks of treatment. The patient seems to be compliant with her medication and experiences no significant side effects. She has no other medical issues and takes no other medications. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely combination of changes in response to this patient’s treatment (AT = angiotensin)?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 38 of 40
38. Question
A 36-year-old woman with end-stage renal disease secondary to type 1 diabetes mellitus comes to the office for routine examination. The patient’s medical history includes hypertension, diabetic retinopathy, and neuropathy. Hemodialysis was started 2 months ago along with an erythropoiesis-stimulating agent. She takes daily long- and short-acting insulin, lisinopril, and calcitriol. Her hemoglobin has increased from 7.4 g/dL to 10.2 g/dL over the past 2 months. Which of the following complications is most likely to be seen with the agent used to treat this patient’s anemia?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 39 of 40
39. Question
A 30-year-old man presents to your office with fatigue, muscle weakness and occasional headaches. His blood pressure is 180/110 mmHg and his heart rate is 80/min. Laboratory evaluation reveals low serum potassium, severely depressed plasma renin activity, and a CT scan demonstrates a right-sided adrenal mass. After treatment for several weeks, the patient’s symptoms resolve, his blood pressure is decreased to 130/70 mmHg and his heart rate is 75/min. Which of the following drugs was most likely used in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 40 of 40
40. Question
A 46-year-old man comes to the emergency department with flank pain and hematuria. The pain is similar to several previous episodes of kidney stones. Abdominal imaging reveals a radiopaque calculus in the right ureter. The patient is admitted to the hospital and given intravenous hydration and analgesics. He subsequently passes the stone with rapid relief of his symptoms. Chemical analysis reveals that the stone is composed primarily of calcium oxalate. Which of the following medications is most likely to prevent recurrent stone formation in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect
