Time limit: 0
Quiz Summary
0 of 17 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Quiz complete. Results are being recorded.
Results
0 of 17 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- NBME 7 BLOCK 4 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 17
1. Question
A 10-minute-old boy is being evaluated in the delivery room. The patient was born at term to a 30-year-old primigravida woman. Pregnancy was unremarkable, but labor was complicated by recurrent late decelerations necessitating vacuum assistance for vaginal delivery. Apgar scores were 6 and 8 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. Temperature is 37 C (98.6 F), pulse is 170/min, and respirations are 40/min. Scalp examination shows large, fluctuant swelling at the occiput that extends bilaterally to the ears, superiorly toward the crown, and inferiorly into the nape of the neck. This patient’s hemorrhage is most likely located between which of the following structures?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 17
2. Question
A 65-year-old man comes to the office with a 4-month history of persistent left ear pain that is slowly worsening. He is also having some difficulty swallowing. The patient has no chronic medical conditions but has smoked 1 pack of cigarettes per day for the last 46 years. On examination, the external auditory canal is patent and the tympanic membrane is clear with no middle ear effusion. There is an enlarged lymph node in the left anterior neck. Flexible fiberoptic laryngoscopy reveals an ulcerative mass on the posterior pharyngeal wall of the hypopharynx. Involvement of which of the following nerves is most likely responsible for this patient’s ear pain?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 17
3. Question
A 28-year-old woman comes to the office due to right hand tremors for the past several weeks. The patient has difficulty performing daily activities and feels embarrassed in social gatherings. She has a history of the remitting-relapsing form of multiple sclerosis. There is no family history of tremors. On physical examination, no abnormal hand movement is observed at rest. When the patient is instructed to touch an object on the table, a coarse tremor is observed that gradually increases as the hand moves closer to its target. Dysfunction of which of the following structures is the most likely cause of this patient’s tremor?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 17
4. Question
A 28-year-old man experiences worsening tinnitus and hearing loss. MRI of the brain reveals bilateral vestibular schwannomas. Genetic testing confirms a diagnosis of neurofibromatosis type 2. Additional imaging reveals a small meningioma at the C5 spinal level impinging upon the medial portion of the dorsal columns. Which of the following is the most likely earliest clinical manifestation of this lesion?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 17
5. Question
A 58-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to a 3-hour history of abrupt-onset weakness and numbness of the right lower extremity, as well as urinary incontinence. Two months ago, the patient was hospitalized due to left-sided weakness that resolved spontaneously after several hours. At that time, MRI of the head and MR angiography of the head and neck were normal, but the patient was found to have atrial fibrillation. An oral anticoagulant was prescribed at discharge, but the patient has been nonadherent with therapy. Blood pressure is 162/94 mm Hg and pulse is 102/min and irregularly irregular. Physical examination shows weakness and sensory loss in the right lower extremity. Babinski sign is present on the right. Speech is normal, and there is no facial weakness. Examination of the right upper extremity and the left extremities is unremarkable. An embolic occlusion affecting which of the following vascular regions is the most likely cause of this patient’s current symptoms?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 17
6. Question
A 64-year-old man with a history of uncontrolled hypertension comes to the emergency department due to sudden-onset, right-sided weakness. Blood pressure is 170/106 mm Hg. Examination shows left facial weakness affecting the forehead and lower face. Muscle strength is 3/5 in the right upper and lower extremities. Deep tendon reflexes are brisk and Babinski sign is present on the right. A midline, sagittal section of a normal brain is shown below:

This patient’s lesion is most likely located at which of the following anatomic locations?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 17
7. Question
A 60-year-old man comes to the office for a follow-up appointment. The patient underwent coronary catheterization 2 weeks ago due to anginal symptoms and had stenting of the left circumflex artery. He has had no chest pain but reports a dark spot in the upper part of his vision since the procedure. The spot disappears when the patient covers the right eye. Medical history also includes hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. On physical examination, visual acuity is normal bilaterally. Computerized visual field testing shows the following finding (dark area representing region of vision loss):
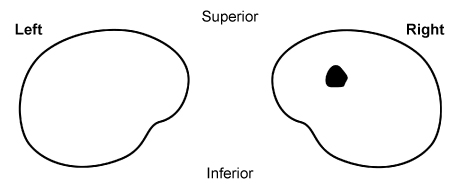
Occlusion of an artery supplying which of the following structures is the most likely cause of this patient’s symptoms?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 17
8. Question
A 74-year-old man with metastatic lung cancer is brought to the emergency department due to sudden-onset severe headache, nausea, and vomiting. The patient was diagnosed with squamous cell lung cancer 4 months ago and was found to have metastasis to the right frontal lobe of the brain. He refused chemotherapy and radiation treatments and is receiving palliative care. Blood pressure is 142/86 mm Hg, pulse is 100/min, and respirations are 20/min. On examination, the patient is somnolent but wakes up to voice and follows instructions. Urgent CT scan of the head reveals hemorrhage within the tumor, causing significant surrounding edema; the right cingulate gyrus is seen herniating beneath the falx cerebri. Which of the following findings is most likely to be present in this patient given his neuroimaging results?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 17
9. Question
A 28-year-old man comes to the emergency department after sustaining an accidental penetrating injury to the left eye. Examination shows left globe perforation with decreased visual acuity. The right eye is normal. The patient is otherwise healthy. Surgical treatment is performed with subsequent improvement in vision. Two months later, the patient experiences pain, photophobia, and diminished vision in the right eye. Evaluation shows leukocytes in the anterior chamber and vitreous humor and choroidal deposits consistent with granulomatous panuveitis. Disruption of which of the following immune processes is most likely responsible for this patient’s current condition?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 17
10. Question
A 23-year-old asymptomatic male participates in clinical research and is found to be homozygous for the apolipoprotein E-4 allele. In the future, this patient is most likely to suffer from which of the following?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 17
11. Question
A 12-year-old girl with intellectual disability is brought to the office for evaluation of recurrent generalized seizures. The patient takes multiple antiepileptic medications. Physical examination shows several hypopigmented skin macules and the findings seen in the exhibit. Brain imaging reveals periventricular subependymal nodules. This patient’s genetic defect directly affects function of which of the following cellular components?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 17
12. Question
A neonate at 38 weeks gestation is delivered vaginally following an uncomplicated pregnancy. Immediately after delivery, the neonate has respiratory distress. Examination shows cyanosis, tachypnea, and poor perfusion. The patient is emergently intubated, and mechanical ventilation is initiated. A nasogastric tube is also inserted. On auscultation, asymmetric aeration with decreased left-sided breath sounds are noted. The abdomen is scaphoid. A chest x-ray is shown in the exhibit. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s respiratory distress?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 17
13. Question
A 14-year-old boy presents with nausea, vomiting, generalized headache, ataxia, and visual complaints. The headaches have awoken him nightly for the past six weeks. MRI reveals a cystic tumor in the cerebellum. Biopsy of the tumor reveals a well-differentiated neoplasm comprised of spindle cells that have hair-like glial processes and are associated with microcysts. These cells are mixed with Rosenthal fibers and granular eosinophilic bodies. Based on these findings, the most likely diagnosis is which of the following?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 17
14. Question
A 25-year-old woman, gravida 1 para 1, comes to the office with her husband for an 8-week postpartum visit. The pregnancy and delivery were normal and without complications. The patient says, “I’m exhausted and sleep deprived but doing okay.” Her husband is concerned about her extreme fatigue; he says she has gotten weaker and unsteady over the past week. He also says she has not been holding the baby as often and rarely goes upstairs to the nursery. The patient reports no depressed mood or appetite changes. Medical history is unremarkable. Blood pressure is 126/84 mm Hg, and pulse is 80/min. On physical examination, the patient appears tired. There is no scleral icterus, and the mucous membranes are pink and moist. The thyroid is not enlarged. Heart and lung sounds are normal, and the abdomen is soft and nontender. There is bilateral lower extremity weakness, left side more than right. Knee reflexes are increased bilaterally. Genital examination shows the episiotomy site has healed, and there is no vaginal discharge. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 17
15. Question
A 36-year-old nulligravid woman comes to the clinic for preconception counseling due to advanced maternal age. The patient has epilepsy that is well controlled on several antiepileptic medications. Her husband has no medical conditions. Temperature is 37.2 C (99 F), blood pressure is 128/76 mm Hg, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 16/min. Examination shows a yellow-brown plaque with irregular borders measuring about 6 cm in diameter along the lower back. There are a few periungual fibromas on the hands and feet. Assume that the patient is heterozygous for her underlying disorder and that the couple will give birth to a boy. Which of the following is the likelihood that the boy will have this disorder?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 17
16. Question
A 31-year-old woman at 12 weeks gestation comes to the office for recurrent headaches. The patient has a history of episodic migraines that typically resolve with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; but since becoming pregnant, the headaches have become more severe and frequent. Over the past month, the patient has had 5 migraine headaches with associated nausea and vomiting that required treatment in the emergency department. In addition, she has had to go to a dark room and rest for a few hours before recovering. The patient has no other chronic medical conditions and her only other medication is a daily prenatal vitamin. Temperature is 36.7 C (98 F), blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, and pulse is 76/min. Fetal heart rate is 160/min. Cranial nerves are intact. Deep tendon reflexes are 2+. Strength and sensation are normal in all extremities. Which of the following is the most appropriate preventive therapy for this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 17
17. Question
A 17-year-old primigravida at 29 weeks gestation comes to the clinic due to headaches. For the last 2 weeks, she has had an intermittent throbbing pain in the left frontal region when she wakes up. The pain is sometimes accompanied by a rhythmic pulsating sound. Acetaminophen provides minimal improvement. The patient has had no fever, right upper quadrant pain, contractions, or vaginal bleeding. She recalls no trauma and has no chronic medical conditions. Prepregnancy BMI is 31 kg/m2, and the patient has gained 20 kg (44 lb) so far. Temperature is 37.1 C (98.8 F), blood pressure is 136/76 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 18/min. Fetal heart rate is 160/min. There is no neck stiffness. Visual field testing is normal. Funduscopic examination shows bilateral optic disc edema. Bilateral deep tendon reflexes are 2+. The remainder of the neurologic examination is unremarkable. Urinalysis has trace protein. Which of the following is the best next step in evaluation of this patient?
CorrectIncorrect
