Time limit: 0
Quiz Summary
0 of 40 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Quiz complete. Results are being recorded.
Results
0 of 40 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 40
1. Question
A 43-year-old man comes to the office due to shortness of breath. For the past 3 months, he has had increasing dyspnea with moderate exertion and is now able to walk only several hundred feet before he has to stop to catch his breath. The patient occasionally wakes from sleep with acute dyspnea, but there is no associated cough, wheezing, or chest pain. Medical history is unremarkable, and he does not smoke. Blood pressure is 124/78 mm Hg, pulse is 106/min, and respirations are 18/min. BMI is 21 kg/m2. Examination shows cracking around the lips. The lungs are clear to auscultation. The heart has a regular tachycardia with an audible S3 and prominent lower sternal heave. The skin of the hands and forearms is dry, smooth, and shiny with patchy loss of pigmentation. Which of the following autoantibodies is most likely present in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 40
2. Question
A 52-year-old woman comes to the office due to breast pain and swelling that started 5 weeks ago. Two weeks ago, her primary care physician scheduled a mammogram and prescribed an oral antibiotic for a breast infection, but the patient’s symptoms have worsened. She has not noticed a mass or lump in her breast, but her nipple has persistent blistering. The patient has diet-controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus. She underwent menopause a year ago and has mild menopausal symptoms but takes no systemic hormone therapy. She had a normal Pap test 3 years ago and has never had a mammogram. The patient has 2 teenaged children. Temperature is 37.2 C (99 F), blood pressure is 130/70 mm Hg, and pulse is 84/min. BMI is 34 kg/m2. The left breast appears diffusely enlarged with thickened, erythematous skin in the entire right upper quadrant and periareolar area. Crusting and erosion of the left nipple are noted. No discrete breast masses are palpable. Several left axillary lymph nodes are enlarged. Right breast examination is normal. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 40
3. Question
A 78-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by ambulance after collapsing in his bathroom. The patient says that about an hour ago he had 2 large-volume bloody stools and felt lightheaded and passed out while trying to get up from the commode. He does not know how long he was unconscious but was able to call 911. The patient has had no chest pain, shortness of breath, abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting. Medical history is significant for coronary artery disease, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and osteoarthritis. He had a coronary stent placed 6 years ago and underwent right-sided total hip replacement 2 years ago. Medications include aspirin, carvedilol, lisinopril, atorvastatin, and acetaminophen as needed. At the field, blood pressure was 90/62 mm Hg and pulse was 110/min. In the emergency department, blood pressure is 104/75 mm Hg and pulse is 98/min and regular. The abdomen is nondistended, soft, and nontender. No hepatosplenomegaly is present. Rectal examination reveals maroon-colored liquid stool with no mass or tenderness. Nasogastric lavage yields yellow aspirate. Hemoglobin is 12.0 g/dL, blood urea nitrogen is 18 mg/dL, and serum creatinine is 1.0 mg/dL. Intravenous fluids are administered. Over the next several hours, vital signs remain stable and there is no further bleeding. The patient asks if he needs any further testing. Which of the following is the most appropriate response?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 40
4. Question
A 62-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to a 3-day history of fever and progressive right leg pain, swelling, and redness. Approximately 2 months ago, the patient had similar symptoms that improved after antibiotic treatment. He has had no chest pain or shortness of breath. His medical problems include hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and coronary artery disease. Seven years ago, he received coronary artery bypass surgery using the right saphenous vein for grafting. The patient does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Temperature is 38 C (100.4 F), blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg, and pulse is 90/min. BMI is 32 kg/m2. Neck veins are flat. Lung fields are clear and heart sounds are normal. Right lower extremity examination shows bright erythema, mild swelling, and tenderness extending from the foot to the mid calf. There is scaling and fissuring between the toes, and the toenails are yellow-colored and thick. Leukocyte count is 14,000/mm3. Imaging studies reveal no focal pus collections, and Doppler ultrasonography is negative for deep venous thrombosis. Cultures are obtained and empiric antibiotics are initiated. Which of the following is the best additional intervention most likely to prevent recurrences of this patient’s current condition?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 40
5. Question
A 19-year-old man comes to the office due to worsening acne. The patient initially had symptoms involving the face and started treatment with topical benzoyl peroxide and topical tretinoin, but he had no relief. Over the past 2 months, the acne has spread to the back, causing local discomfort. The patient is otherwise healthy. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Vital signs are within normal limits. Skin examination of the face, shoulders, and back reveal similar lesions as shown in the image below:

Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 40
6. Question
A 34-year-old female has had five urinary tract infections over the last two months. She also complains of a decreased appetite and occasional nausea. She has had diarrhea accompanied by lower abdominal pain for the past year. Her other complaints include palpitations, difficulty sleeping, and chronic low back pain. She also thinks that she has lost some weight recently. She smokes one pack of cigarettes per day and has for the past ten years. She takes no medications besides a daily multivitamin supplement. Her last urine culture grew mixed flora including Escherichia coli and Bacteroides fragilis. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 40
7. Question
A 43-year-old woman, gravida 2 para 2, comes to the office for evaluation of heavy menstrual bleeding. Previously, menses were every 30 days and lasted 3-4 days, with 1 day of heavier bleeding. For the past 4 months, her periods have lasted 6-7 days, with heavy bleeding for 4 days requiring a thick pad every few hours. The patient has also noticed intermenstrual bleeding. She has no abdominal pain, weakness, or urinary symptoms. Her medical problems include hypothyroidism, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes mellitus; all are currently controlled on oral medications. Her last Pap test 2 years ago was normal, and she has no history of abnormal Pap results. She is sexually active with one partner and had a bilateral tubal ligation. The patient has no history of sexually transmitted infections. Family history is significant for colon cancer in her mother at age 67. The patient does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Blood pressure is 146/72 mm Hg and pulse is 62/min. BMI is 35 kg/m2. Laboratory results are as follows:
Hemoglobin
10.8 g/dL
Mean corpuscular volume
79 fL
Platelets
300,000/mm3
TSH
4.2 µU/mL
Urine pregnancy test is negative. Pelvic ultrasound reveals several uterine fibroids, the largest of which measures 6 cm in diameter. Which of the following best addresses this patient’s condition?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 40
8. Question
A 46-year-old man comes to the office to follow up on his hypertension. During an office visit a year ago, his blood pressure was 138/88 mm Hg, and lifestyle modification was advised. The patient has been restricting dietary sodium, consuming more fruits and vegetables, and exercising regularly. Since that time, his blood pressure has consistently been between 138/88 mm Hg and 142/92 mm Hg. The patient has had no chest pain, shortness of breath, headache, dizziness, or focal weakness or numbness. Two years ago, he experienced severe pain at the right great toe and was diagnosed with acute gout that responded to colchicine. Since then, the patient reduced his alcohol intake and has had only one additional mild gout attack. He has no other medical conditions and takes no medications. Blood pressure today is 142/92 mm Hg in the right arm and 144/93 mm Hg in the left. Temperature is 36.6 C (97.9 F), pulse is 76/min and regular, and respirations are 14/min. BMI is 29 kg/m2. Neck veins are flat, the lungs are clear, and heart sounds are normal; abdominal examination reveals no abnormalities. There is no edema in the lower extremities. ECG shows normal sinus rhythm with no significant abnormalities. Laboratory results are as follows:
Complete blood count
Hemoglobin
13.4 g/dL
Platelets
350,000/mm³
Leukocytes
8,600/mm³
Serum chemistry
Sodium
142 mEq/L
Potassium
4.5 mEq/L
Bicarbonate
24 mEq/L
Blood urea nitrogen
16 mg/dL
Creatinine
0.8 mg/dL
Calcium
9.3 mg/dL
Glucose
98 mg/dL
Uric acid
5.8 mg/dL
Urinalysis
Protein
none
Blood
negative
Casts
none
Which of the following is the best initial pharmacotherapy for management of this patient’s hypertension?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 40
9. Question
The following vignette applies to the next 2 items. The items in the set must be answered in sequential order. Once you click Proceed to Next Item, you will not be able to add or change an answer.
A 65-year-old male is brought to the emergency room by ambulance for right lower quadrant abdominal pain and right groin pain for the past two hours. He states that he was working in his garden when he suddenly felt a severe pain on his right side. He went inside to lie down, but the pain persisted. He is also feeling light-headed and short of breath. He denies fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, chest pain, or diarrhea. He has not noticed any blood in his stool or urine. His past medical history is significant for atrial fibrillation, hypertension, and coronary artery disease. Current medications include warfarin, lisinopril, metoprolol, and aspirin. He is allergic to sulfa. He does not smoke, and drinks alcohol socially. Vital signs on arrival to the ER are temperature 36.5°C (97.7°F), pulse 110/min, respiratory rate 18/min, blood pressure 89/52 mmHg, and oxygen saturation 94% on 2 liters oxygen via nasal cannula. On examination, he appears to be in mild distress and is fatigued. Heart sounds are normal except for tachycardia. Lungs are clear to auscultation bilaterally. The abdomen is soft and nondistended. There is pain to palpation in the right lower quadrant, but no rebound tenderness. There is severe pain in the right lower quadrant upon flexion of the right hip. There is no calf tenderness or lower extremity edema. Laboratory studies show:
Hematocrit
27%
MCV
89 fl
Leukocyte count
6000/mm3
Platelets
350,000/mm3
PTT
26 seconds
PT
18 seconds
INR
2.7
Sodium
140 mEq/L
Potassium
3.9 mEq/L
Chloride
100 mEq/L
Bicarbonate
23 mEq/L
BUN
38 mg/dL
Creatinine
1.5 mg/dL
Glucose
106 mg/dL
Calcium
9.0 mg/dL
Lactic acid
1.1 mmol/L
A urinalysis is normal and an ECG shows atrial fibrillation with a ventricular rate of 112/min.
Item 1 of 2
What is the best initial diagnostic test for this patient’s condition?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 40
10. Question
Item 2 of 2
The diagnosis is confirmed after the appropriate diagnostic test is done. After 2 liters of normal saline are given, repeat vital signs are temperature 36.8 C (98.2 F), blood pressure is 103/62 mm Hg, pulse 95/min, and respirations are 16/min. The patient continues to have moderate pain in the right lower quadrant. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 40
11. Question
A 45-year-old man has been hospitalized for the past 2 days due to pneumonia. The patient has received intravenous antibiotics and oxygen therapy with little improvement in shortness of breath or cough. Medical history is significant for cocaine use disorder, remitted major depressive disorder, hepatitis C, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and mild intellectual disability. The patient lives independently. Temperature is 38.9 C (102 F), blood pressure is 97/56 mm Hg, pulse is 115/min, and respirations are 24/min. Examination reveals bibasilar crackles and mild diffuse wheezing. Chest x-ray shows worsening bibasilar opacities. The physician explains that the patient’s pneumonia is worsening and that he will need several more days of intravenous antibiotics and close monitoring in the hospital. The patient is able to demonstrate an understanding of the proposed treatment. However, after discussion, he adamantly refuses further treatment and wants to be discharged immediately. He understands that his condition may worsen when he leaves the hospital but wants to be released anyway. His brother and sister are at his bedside. Although they would like him to receive treatment, they believe that his decision is consistent with his values. Montreal Cognitive Assessment is 25/30 (normal: ≥26). Which of the following is the most appropriate course of action?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 40
12. Question
A 32-year-old woman comes to the office due to low mood and fatigue for the past 2 months. The patient wakes up at 3:00 AM and has difficulty falling back asleep each night, which causes her to feel exhausted during the day. She has an increased appetite, which has resulted in a weight gain of 2.3 kg (5 lb). The patient is a paralegal at a law firm and states that she has been unable to keep up with her workload. She says her life “has no purpose” but has no suicidal thoughts. The patient drinks a glass of wine 2 or 3 times a week and does not smoke cigarettes or use recreational drugs. She has no chronic medical conditions, and her only medication is a combined estrogen-progestin oral contraceptive. Family history is significant for depression in her mother and sister. Vital signs are normal. Physical examination is unremarkable. Mental status examination reveals a flat affect but normal attention and memory. Which of the following is required prior to prescribing appropriate pharmacotherapy for this patient’s depressive symptoms?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 40
13. Question
A 9-year-old boy with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is brought to the office by his mother for an annual physical examination. His ADHD has been treated with several methylphenidate and amphetamine preparations with moderate improvement. He is less fidgety and hyperactive overall and is able to remain seated in the classroom. However, he is still easily distracted and has difficulty completing his work on time. The boy is about to begin the school year, and his mother is concerned that he will not perform well due to his ADHD. She has asked his teacher if he can receive additional time to complete his work. The teacher responded that she will not be able to give him special allowances as this would be unfair to the other children. The patient’s mother asks the physician to call the school and explain the patient’s illness to the principal so that the child can get help in the classroom. Which of the following is the most appropriate response to the mother’s request?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 40
14. Question
An 89-year-old woman is brought to the office by her niece due to increasing confusion over the last 2 weeks. The patient lives alone, but the niece visits her frequently. The patient has no history of dementia and was able to perform all activities of daily living until 2 weeks ago. Since then, her appetite has been poor and she has not been eating or drinking as much. The patient has also developed urinary incontinence in the last few days. She ambulates using a cane and has had no falls recently. Medical history is significant for hypertension for which she takes hydrochlorothiazide and for breast cancer treated 3 years ago with right-sided mastectomy and radiation therapy. The patient has a history of smoking in the remote past but quit in her 20s, and does not drink alcohol. Temperature is 36.5 C (97.7 F), blood pressure is 104/62 mm Hg, pulse is 95/min, and respirations are 12/min. The patient appears fatigued and is oriented to person, but not place or time. Mucous membranes are dry. The lungs are clear to auscultation and heart sounds are normal. There is no peripheral edema. Neurologic examination shows no focal deficits. Urinalysis shows a specific gravity of 1.004 with negative nitrite, no leukocyte esterase, white blood cell count 0-2/hpf, and few epithelial cells. ECG shows sinus rhythm with shortening of the QT interval. Which of the following electrolyte abnormalities is the most likely cause of this patient’s altered mental status?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 40
15. Question
A 52-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to chest pain for the past 2 hours. He was dining at a local restaurant when he experienced sudden-onset midline chest pain and shortness of breath. The patient describes the pain as pressure that fluctuates in intensity but does not go away. He also began sweating profusely when the pain started. He has had no palpitations, dizziness, or loss of consciousness. Medical history is significant for hypertension; the patient admits nonadherence with prescribed medications. He smokes a pack of cigarettes daily and drinks alcohol occasionally. Family medical history is significant for stroke in his father at age 57. Blood pressure is 156/94 mm Hg in the right arm and 152/90 mm Hg in the left, and pulse is 100/min and regular. The lungs are clear to auscultation. ECG obtained in the emergency department is shown in the exhibit. Initial cardiac troponin level is negative. Chest x-ray is unremarkable. Sublingual nitroglycerin, chewable aspirin 325 mg, and oral metoprolol are given. Which of the following represents the best next steps in management of this patient?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 40
16. Question
An 18-month-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his parents due to several episodes of nonbloody, nonbilious emesis over the past 12 hours. During this time, he has also had intervals of inconsolable crying. The patient has had no diarrhea, but his last 2 bowel movements appeared much darker than usual. The last food he ate was a bite of a hamburger approximately 6 hours ago. The patient takes no medications and has no allergies. He does not attend day care and has not traveled outside the United States. Temperature is 36.8 C (98.2 F), blood pressure is 80/45 mm Hg, pulse is 146/min, and respirations are 24/min. Examination shows a tired-appearing boy with dry mucous membranes. No murmurs or adventitious breath sounds are heard on auscultation. The abdomen is soft, but there is some fullness and tenderness to palpation in the right lower quadrant. Bowel sounds are heard in all quadrants. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 40
17. Question
The following vignette applies to the next 2 items. The items in the set must be answered in sequential order. Once you click Proceed to Next Item, you will not be able to add or change an answer.
An 82-year-old woman, who resides in a nursing home, is brought to the emergency department with cough, wheezing, and mild shortness of breath. Medical history is significant for hypertension, hyperlipidemia, coronary artery disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and right knee osteoarthritis. The patient had a coronary artery stent placed 10 years ago and a left-sided carotid endarterectomy 7 years ago after an episode of transient aphasia. Surgical history is also significant for cholecystectomy. Temperature is 37.2 C (99 F), blood pressure is 142/87 mm Hg, and pulse is 98/min. Chest x-ray reveals dense left lower lobe consolidation. The patient is admitted to the hospital and treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics and fluids. A Foley catheter is placed for a day and then removed. On the third day of hospitalization, the patient feels better; her cough has decreased in intensity, and her breathing has improved. However, she feels weak and mildly dizzy when she moves from the bed to a chair. She tolerates oral feedings with no difficulties but also has mild nausea and 2 or 3 episodes of loose stools. On the fourth day of hospitalization, she is lethargic. Current temperature is 38.3 C (100.9 F), blood pressure is 122/78 mm Hg, and pulse is 110/min and regular in rhythm. Leukocytes are 28,000/mm3 (13,000/mm3 on admission), and platelets are 550,000/mm3 (230,000/mm3 on admission).
Item 1 of 2
Which of the following is the most likely finding on physical examination of this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 18 of 40
18. Question
Item 2 of 2
Over the next 5 hours, the patient becomes hypotensive and requires high-volume intravenous fluid resuscitation. She is transferred to the intensive care unit for further management. Which of the following would be the most appropriate next step in diagnosing the cause of this patient’s deterioration?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 40
19. Question
A 40-year-old woman comes to the office for a routine preventive visit. She feels well. Medical history is unremarkable. The patient does not use tobacco or alcohol. She eats a diet rich in fruits and vegetables. Her mother died of a stroke at age 69, and her father has coronary artery disease. Initial blood pressure is 148/92 mm Hg and pulse is 74/min. Physical examination is unremarkable. Following the examination, repeat blood pressure measurement is 146/90 mm Hg. Previous measurements in the office 6 months ago were similar. However, the patient reports that she measures her blood pressure at home at least 3 times a week with a maximum pressure of 125/75 mm Hg. Which of the following is the most appropriate statement to make to this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 40
20. Question
A 33-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by ambulance after a syncopal episode at a local shopping mall. He felt lightheaded and nauseated before the event. Over the last few weeks, the patient has experienced fatigue and decreased appetite. He has no chest pain, cough, wheezing, fever, chills, or headaches. He has never before experienced syncope. He has no history of heart disease or seizures. The patient was treated a year ago for non-Hodgkin lymphoma with radiation and combination chemotherapy that included an anthracycline. He recently finished a 30-day course of antibiotics for prostatitis and is not taking any medications currently. His father died suddenly of a presumed heart attack at age 46, and his mother suffered a stroke at age 57. The patient has no known drug allergies. Temperature is 37.2 C (99 F), blood pressure is 96/52 mm Hg, pulse is 90/min and regular, and respirations are 18/min. Oxygen saturation is 97% on room air. Jugular venous pulsation is visible approximately 10 cm above the sternal angle. The lungs are clear to auscultation. The abdomen is soft and nontender. There is trace peripheral edema bilaterally. ECG is shown in the exhibit. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s syncopal episode?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 21 of 40
21. Question
A 72-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to lower abdominal pain and difficulty voiding for the past 2 days. During this time, the patient’s urine stream has reduced to a dribble and he has passed only very small amounts of urine. Medical history includes hypertension, benign prostatic hyperplasia, and gout; current medications include lisinopril, tamsulosin, and allopurinol. For the past week he has also been taking over-the-counter nasal decongestants and antihistamines due to an upper respiratory infection. The patient does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Temperature is 36.6 C (97.9 F), blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg, pulse is 92/min, and respirations are 16/min. He appears to be in moderate distress. The lungs are clear on auscultation, and heart sounds are normal. The abdomen is soft and nondistended. There is moderate suprapubic tenderness. The prostate is enlarged, smooth, and nontender. There is no lower extremity edema. Urinary catheterization yields 2,000 mL of straw-colored urine. Urinalysis is negative for leukocyte esterase or nitrites. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 22 of 40
22. Question
A 62-year-old woman comes to the clinic due to bilateral shoulder pain over the last 6 months. She describes the pain as an achy stiffness that interferes with her daily activities, especially in the morning. Because of the pain, it takes significant effort for the patient to pull on socks and fasten her bra. She denies fever, chills, headache, jaw pain, vision problems, or hearing loss. Medical history is significant for moderate, persistent asthma; hypertension; and hyperlipidemia. The patient had a total right knee replacement for osteoarthritis 3 years ago. After the surgery, she had deep venous thrombosis and anticoagulation with warfarin for 6 months. Family history is significant for hypertension and coronary artery disease. The patient’s mother had rheumatoid arthritis and was disabled due to pain and joint deformities. Blood pressure is 145/91 mm Hg and pulse is 82/min. On examination, there is decreased range of motion of both shoulders, with some local tenderness to palpation. There is no muscle weakness or sensory loss. While discussing the treatment options with this patient, which of the following should be emphasized?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 23 of 40
23. Question
A 68-year-old man comes to the office for a routine follow-up visit. He has had mild fatigue but no chest pain, shortness of breath, or palpitations. The patient has a history of hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, coronary artery disease, and chronic kidney disease. He underwent coronary artery bypass surgery 10 years ago. The patient says, “I regularly check my blood pressure and fingerstick glucose at home. My blood pressure used to be much higher.” Current medications include aspirin, metoprolol, lisinopril, diltiazem, empagliflozin, insulin glargine, atorvastatin, sevelamer, and calcitriol. Blood pressure is 124/73 mm Hg and pulse is 78/min. BMI is 20.5 kg/m2. There is no jugular venous distension. The lungs are clear and no abnormal heart sounds are present. Laboratory results are as follows:
Complete blood count
Hemoglobin
11.6 g/dL
Mean corpuscular volume
92 µm3
Platelets
305,000/mm3
Leukocytes
8,800/mm3
Serum chemistry
Sodium
142 mEq/L
Potassium
4.3 mEq/L
Bicarbonate
19 mEq/L
Blood urea nitrogen
26 mg/dL
Creatinine
3.8 mg/dL
Calcium
8.6 mg/dL
Phosphorus
4.2 mg/dL
Glucose
110 mg/dL
Estimated glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is 20 mL/min/1.73 m2. Over the past year, the patient’s serum creatinine level has been 3.5-4.3 mg/dL and estimated GFR 17-25 mL/min/1.73 m2. The level of proteinuria is determined to be 1.2 g/day. Which of the following is currently the best recommendation for this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 24 of 40
24. Question
A 2-year-old boy is brought to the office due to fever, runny nose, and cough over the past 4 days. For the past 2 days, he has been crying more frequently and has had decreased appetite; today he had an episode of emesis. The patient has had 2 previous episodes of acute otitis media, but he has no chronic medical issues and takes no medications. His immunizations are up to date. Growth percentiles and developmental milestones are appropriate for age. He lives with his parents, both of whom are in good health, and he attends day care 5 days a week. There are no carpets or pets in the home. Temperature is 38.3 C (101 F), pulse is 120/min, and respirations are 20/min. The patient is awake and alert but is fussy and crying. The head is normocephalic and atraumatic. Nasal turbinates are erythematous with copious drainage; the pharynx demonstrates mild erythema and thick white postnasal drip. Otoscopy reveals a bulging, erythematous left tympanic membrane and an erythematous right tympanic membrane. Which of the following is most likely to occur in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 25 of 40
25. Question
An 87-year-old female presents with two days of cough, fever, and mild shortness of breath. On review of systems, she also notes several months of fatigue. Her past medical history is significant for hypertension, chronic back pain, and a stroke two years ago without residual neurologic deficits. She does not smoke or consume alcohol. Her temperature is 38.3°C (101°F), blood pressure is 143/92 mmHg, and heart rate is 94/min. Examination reveals coarse rhonchi over the right lower lobe. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin
8.1 g/dL
MCV
89 fl
Leukocyte count
13,500/mm3
Neutrophils
73%
Bands
6%
Platelets
255,000/mm3
Sodium
136 mEq/L
Potassium
4.2 mEq/L
Bicarbonate
23 mEq/L
Chloride
98 mEq/L
Calcium
10.7 mg/dL
BUN
14 mg/dL
Creatinine
1.4 mg/dL
Total protein
7.5 g/dL
Albumin
3.4 g/dL
AST
32 U/L
ALT
24 U/L
Alkaline phosphatase
110 U/L
Which of the following is most likely to reveal the cause of this patient’s anemia?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 26 of 40
26. Question
A 26-year-old man comes to the office due to scrotal discomfort for the past several weeks. The patient says, “I have been getting a dragging sensation and heaviness in my left scrotum, especially in the evening after work.” He has no chronic medical problems and takes no medications. The patient is sexually active with his girlfriend, who takes an oral contraceptive. He smokes a pack of cigarettes a day and drinks 2 or 3 cans of beer on weekends. The patient works as a machine operator at a factory, which requires standing on his feet for prolonged periods and occasional lifting of heavy objects. His father was diagnosed with prostate cancer at age 60. Vital signs are within normal limits. The abdomen is nondistended, soft, and nontender with no inguinal mass or lymphadenopathy. Examination of the external genitalia shows no penile discharge, ulceration, or lesions. There is an irregular, soft, left-sided scrotal mass that appears with Valsalva maneuver and completely disappears with recumbency. Right scrotal examination is normal. Which of the following is the most appropriate response to the patient regarding his current condition?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 40
27. Question
A 6-hour-old girl is evaluated in the newborn nursery due to difficulty feeding. The infant was born at 39 weeks gestation to a 26-year-old woman, gravida 2 para 2, via spontaneous vaginal delivery. Routine prenatal serologic testing was negative. Rectovaginal culture for group B Streptococcus was positive at 36 weeks gestation, and the mother received appropriate intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis. Apgar scores at 1 and 5 minutes were 7 and 8, respectively. Birth weight was 2.89 kg (6 lb 6 oz) and length was 51 cm (20 in). The infant’s face turned blue when she was breastfeeding. When removed from the breast, she began crying and “looked pink again,” according to the mother. The infant has had no coughing or choking episodes. Respirations are 24/min, and pulse oximetry is 97% on room air. The skin and mucosa are pink. Mild stertor is heard at the nose and mouth. Cardiac auscultation does not reveal a murmur, and the lungs are clear. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 28 of 40
28. Question
A 61-year-old man comes to the emergency department (ED) following 2 weeks of progressive, exertional shortness of breath. He also reports significant weight loss with reduced appetite over the past 3 months. The patient has no known medical problems and has never seen a primary care physician. He lives alone in a single-bedroom apartment. The patient has smoked a pack and a half of cigarettes daily for the past 42 years. Family medical history is notable for breast cancer in his mother. Vital signs are normal other than an oxygen saturation of 92% while breathing ambient air. On physical examination, there is dullness to percussion as well as decreased breath sounds over the right mid-lower chest. A chest x-ray confirms the presence of a large right-sided pleural effusion. A thoracentesis is performed, and 1.5 liters of yellowish fluid are obtained. Pleural fluid analysis reveals an exudative effusion containing adenocarcinoma cells. The patient symptomatically improves after the procedure with full reexpansion of his lung. A subsequent CT scan of the chest shows a 5-cm mass in the right upper lobe with regional adenopathy, pictured below.
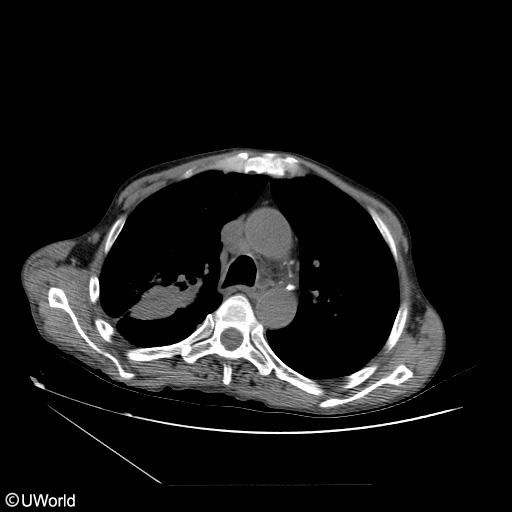
The patient is discharged home with close outpatient follow-up. He comes again to the ED 2 weeks later with similar symptoms after missing his outpatient appointment. A chest x-ray reveals reaccumulation of the pleural effusion. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment option for this patient’s pleural effusion?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 29 of 40
29. Question
A 7-year-old male is brought to your office by his mother for a routine check-up. The mother states that the patient is doing quite well currently and has no specific problems, but she is worried that he may have lead poisoning because she has seen him picking paint off of a wall in his bedroom on several occasions. The house they live in was built in 1922. He has been healthy all of his life and has reached his developmental milestones normally. All of his immunizations are up-to-date, and he takes no medications and has no allergies. On examination, he is in no acute distress and answers questions appropriately. The mucous membranes are moist and there is no pallor. The lungs are clear to auscultation and heart sounds are normal. The blood lead level is 19 mcg/dL. A complete blood count, serum iron level, and serum ferritin concentration are within normal limits. What is the best next step in the management of this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 30 of 40
30. Question
A 63-year-old woman had a short-lived “blackout” while driving, resulting in a minor motor vehicle collision. In the emergency department, she is alert and oriented and reports mild nausea. She has no chest pain, shortness of breath, headache, weakness, or numbness in her extremities. The patient was diagnosed with a urinary tract infection 3 days ago and is being treated with levofloxacin. She also has a history of hypertension. The patient smokes a pack of cigarettes daily, drinks alcohol on weekends, and smokes marijuana occasionally. Blood pressure is 143/89 mm Hg while supine and 148/86 mm Hg while standing. ECG is shown in the exhibit. Which of the following most likely caused this patient’s syncope?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 31 of 40
31. Question
A 57-year-old male is found to have a hard prostate nodule on rectal examination. He denies any urinary complaints, weight loss, cough, shortness of breath, or bone pain. His past medical history is significant for hypertension controlled with hydrochlorothiazide and lisinopril. His father had prostate cancer. Ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy is performed. Histologically, the lesion is a high-grade adenocarcinoma (Gleason score 9). Treatment options are discussed with the patient and he chooses radical prostatectomy. The surgical specimen does not show any evidence of extraprostatic extension. Which of the following is the best follow-up test for this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 32 of 40
32. Question
A 72-year-old man comes to the office due to left hip pain. The pain started 6 months ago as an intermittent, deep ache in the front of the hip that radiates to the groin, and it has since progressed in severity. It is associated with stiffness and is most noticeable after the patient’s morning walks or when he squats down while gardening. There is no history of trauma. Medical history includes hypertension, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and benign prostatic hyperplasia. Family history is notable for rheumatoid arthritis in his father. Medications include lisinopril, pantoprazole, and tamsulosin. Vital signs are within normal limits. On physical examination, the patient has a mildly waddling gait and can walk on heels and toes. There is no pain with forward flexion or extension of the spine. The patient can balance unsupported on each leg; when standing on the left leg, the pelvis tilts to the right. Straight leg raising test is negative on both sides. Musculoskeletal examination of the hip shows limited internal rotation of the left hip, a maneuver that also elicits severe pain in the groin. Which of the following is the best initial test in evaluation of this patient’s pain?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 33 of 40
33. Question
The following vignette applies to the next 2 items.
A 45-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to 10 days of exertional shortness of breath and dry cough. The patient has also lost weight over the last 2 months despite no changes in dietary or exercise habits. He has had no hemoptysis, orthopnea, abdominal pain, or diarrhea. The patient is a former intravenous drug user and is currently in a methadone program. He was diagnosed with HIV infection several years ago but has never received antiretroviral therapy. He also has chronic hepatitis C infection. The patient is homeless. His last emergency department visit was 2 months ago for a skin infection on his right foot, which was treated with a short course of antibiotics. He smokes a pack of cigarettes daily and consumes hard liquor at least twice a week. Temperature is 37.9 C (100.3 F), blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, and pulse is 120/min. Oxygen saturation is 93% on 2 L oxygen by nasal cannula. BMI is 17.5 kg/m2. Oropharyngeal examination shows moist mucous membranes, poor dentition, and white patches on the buccal mucosa. There is palpable anterior cervical lymphadenopathy. Lung auscultation reveals scattered crackles bilaterally. The abdomen is soft and nontender. The liver edge is palpated 3 cm below the right costal margin. No peripheral edema is present. Chest x-ray is shown in the exhibit. ECG shows sinus tachycardia with no significant ST-segment or T-wave changes.

Item 1 of 2
Which of the following is the best next diagnostic step for this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 34 of 40
34. Question
Item 2 of 2
The microbial etiology of this patient’s condition is confirmed by appropriate testing. His leukocyte count is 2,600/mm3, hemoglobin is 9.8 mg/dL, and platelet count is 128,000/mm3. The results of which of the following tests would most likely impact the management of the patient’s infection at this time?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 35 of 40
35. Question
A 63-year-old man is hospitalized due to fever, chills, shortness of breath, and productive cough. The patient has a history of multiple myeloma and recently received a cycle of chemotherapy as an outpatient. He has a 25-pack-year smoking history. Initial laboratory evaluation shows a leukocyte count of 21,000/mm3. Chest x-ray reveals a dense right lower lobe infiltrate. The patient is started on antibiotic therapy. On the third day of hospitalization he develops severe shortness of breath. He is intubated and transferred to the intensive care unit for mechanical ventilation. An internal jugular central venous line is placed for intravenous fluids and antibiotics, and a Foley catheter is inserted to monitor urine output. On day 5 of hospitalization, urinalysis shows 50-100 red blood cells, 10-30 leukocytes, and trace protein. Urine culture grows Candida albicans. He is afebrile and his leukocyte count is now 9,000/mm3. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 36 of 40
36. Question
A 32-year-old man comes to the office due to right ankle pain. During a hockey game the previous evening, the patient experienced sudden inversion of the right foot, which caused immediate severe pain. He had a minor knee injury in the past, but otherwise his medical history is insignificant. On physical examination, there is swelling and bruising on the lateral aspect of the right ankle and foot. The patient is unable to bear weight on the right foot. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 37 of 40
37. Question
A 64-year-old man comes to the office with a 3-month history of cough that is mostly dry but occasionally produces whitish phlegm. He has no fevers, chills, night sweats, or chest pain. The patient reports a 4.5-kg (10-lb) weight loss over the last 2 or 3 months. His medical history is significant for Hodgkin lymphoma treated with combination chemotherapy 5 years ago. He also has hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and hyperlipidemia. The patient’s current medications are hydrochlorothiazide, metoprolol, lisinopril, metformin, pioglitazone, and atorvastatin. He has a 20-pack-year smoking history but quit 7 years ago. Blood pressure is 124/89 mm Hg and pulse is 67/min. BMI is 23 kg/m2. On physical examination, no peripheral lymphadenopathy, skin rash, or joint deformity is present. Breath sounds are decreased over the left mid lung field. Chest x-ray is shown below.

Which of the following most likely accounts for this patient’s current symptoms?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 38 of 40
38. Question
A 32-year-old man comes to the office for a routine preventive examination. He indicates that he generally feels well. He takes omeprazole for gastroesophageal reflux disease. The patient has a 10-pack-year smoking history. He drinks alcohol socially and smokes marijuana occasionally on weekends. His father died of colon cancer at age 61, and his mother has hypertension and rheumatoid arthritis. The patient is allergic to penicillin. Temperature is 36.4 C (97.5 F), blood pressure is 112/69 mm Hg, pulse is 75/min, and respirations are 16/min. Cardiac auscultation reveals a late systolic murmur at the apex. The lungs are clear to auscultation, and there is no peripheral edema. Echocardiography reveals left atrial enlargement, normal left ventricular size, and mitral valve prolapse with moderate mitral regurgitation. Two days later, the patient calls the office to report he is having a root canal early next week and read on the Internet that antibiotics should be taken before the procedure to prevent an infection in heart valves. Which of the following is the most appropriate response to this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 39 of 40
39. Question
A 14-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department by her mother due to concern for a toxic ingestion. The mother states, “I found her in her room crying next to an empty bottle of acetaminophen, but she won’t tell me how much she took.” The patient’s mother is a nurse and says that her daughter has been “sullen” since her father died 2 months ago. When interviewed alone, the girl reports multiple recent stressors, including breaking up with her boyfriend and getting poor grades in school. She says she took “a bunch” of 500-mg acetaminophen tablets 8 hours ago “to make the pain go away.” She has no abdominal pain, vomiting, nausea, coingestions, or prior ingestions. Temperature is 36.1 C (97 F), blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, pulse is 78/min, and respirations are 12/min. Pulse oximetry shows 99% on room air. On physical examination, the patient is calm with a flat affect; she is resting comfortably in the bed and staring at her cell phone. She is alert and oriented to person, place, and time and answers questions appropriately. The abdomen is soft, nontender, and nondistended with normoactive bowel sounds. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 40 of 40
40. Question
A 53-year-old man comes to the office due to upper abdominal discomfort that has been steadily worsening over the past 2 months. The discomfort is constant and dull and radiates to the back. The patient has had no vomiting or diarrhea and has lost 7 kg (15.4 lb) since symptoms began. He has no chronic medical conditions and has never had similar symptoms. The patient has a 40-pack-year history and drinks 1 or 2 beers most days. He has a remote history of injection drug use. Diet consists mostly of fast food and processed meats. He has worked in a rubber factory for the past 10 years. CT scan of the abdomen with intravenous contrast is shown below.

Which of the following is the strongest risk factor for this patient’s current condition?
CorrectIncorrect
