Quiz Summary
0 of 40 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 40 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 40
1. Question
A 66-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to sudden-onset loss of vision in his right eye. The patient states that, 15 minutes ago, his right eye completely “grayed out” within seconds and he is unable to see out of it. He has had no trauma, eye pain, headache, or other neurologic symptoms. He has no history of eye disorders, and medical history includes hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Temperature is 36.5 C (97.7 F), blood pressure is 142/86 mm Hg, and pulse is 80/min. On physical examination, the patient appears anxious. There is no conjunctival erythema. Visual acuity is normal on the left eye but is diminished to hand motion on the right eye. The remainder of the physical examination, including neurologic examination, is normal. Which of the following funduscopic findings is associated with the likely cause of this patient’s vision impairment?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 40
2. Question
A 44-year-old woman comes to the office with muscle weakness over the past several months. She has difficulty combing her hair and, occasionally, difficulty holding up her head, particularly after prolonged sitting or standing. The patient has had no difficulty walking or getting up from a chair. She has also had 2 episodes of double vision while driving home from work. The patient takes rosuvastatin for hyperlipidemia. Blood pressure is 122/80 mm Hg and pulse is 76/min. Neurologic examination shows mild right ptosis, symmetric proximal muscle weakness in the upper extremities, and weakness in the head extensors. Muscle bulk and tone are normal, and there is no muscle tenderness. Which of the following is the most likely site of the pathology in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 40
3. Question
A 32-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department by her husband due to slurred speech and difficulty walking. The patient has also been uncharacteristically drowsy for the past several hours. She has a history of bipolar disorder, insomnia, migraine headaches, seizures, and hypothyroidism. Temperature is 37 C (98.6 F), blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, pulse is 76/min, and respirations are 12/min. The patient is lethargic and falls asleep during the interview and physical examination. Pupils are 3 mm and reactive to light. The neck is supple and the oropharynx is clear. Chest auscultation is unremarkable. The abdomen is soft and nontender; bowel sounds are normal. Limited neurologic examination shows 2+ deep tendon reflexes in all 4 extremities; there is no Babinski sign, and strength is 5 on a scale of 0-5 throughout. No nystagmus or hand tremor is present. Blood glucose is 130 mg/dL. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s symptoms?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 40
4. Question
A 75-year-old man comes to the office due to intermittent right eye vision loss. The patient reports 3 episodes over the past 2 months in which he suddenly experienced “a curtain falling over the right eye” for several minutes before it spontaneously resolved. He has no eye pain or discomfort, focal weakness, numbness, or headache. His medical history is significant for hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and osteoarthritis. He smoked cigarettes for 25 years before quitting at age 50. Blood pressure is 140/85 mm Hg and pulse is 74/min. Visual acuity, pupillary reflex, and funduscopic examinations are unremarkable. Further neurologic examination shows normal reflexes, motor strength, and sensation. Which of the following is most likely to yield the diagnosis in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 40
5. Question
A 73-year-old man comes to the office due to increasing forgetfulness over the past 6 months. He says, “My mind used to be quite sharp, but now I can’t even concentrate to read a book or newspaper. I’m afraid I’m developing dementia like my father.” The patient reports he has been losing sleep and has little energy and motivation. He recently took a leave of absence from work because he could no longer concentrate on details and complete his paperwork. His medical history includes hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes, benign prostatic hyperplasia, and transient ischemic attack. Family history is significant for hypertension and diabetes (mother) and Alzheimer disease (father). The patient does not smoke and drinks wine only occasionally. Vital signs are unremarkable, and physical examination is normal except for slowed speech and movements. The patient declines to perform a serial sevens assessment and says, “I just can’t do it.” CT scan of the head is normal. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s cognitive impairment?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 40
6. Question
A 34-year-old woman comes to the hospital after a day of sudden onset fever, chest tightness, dyspnea, and dry cough. The patient has been hospitalized twice in the past 3 months with similar symptoms. Both times she received antibiotic treatment for pneumonia and the symptoms resolved within 1-2 days. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. She has no known drug allergies. Temperature is 37.9 C (100 F), blood pressure is 128/80 mm Hg, pulse is 92/min, and respirations are 20/min. Pulse oximetry is 90% on room air. BMI is 29 kg/m2. The patient is in mild respiratory distress. Examination shows normal jugular venous pressure, no lymphadenopathy, and normal heart sounds. Diffuse fine crackles are heard throughout both lung fields. Leukocytes are 11,200/mm3. CT scan of the chest reveals a bilateral micronodular interstitial pattern. Blood cultures are negative. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 40
7. Question
A 52-year-old man comes to the emergency department with a 24-hour history of pain and swelling of his right knee. He has no fevers, chills, or recent trauma to the knee. In addition, the patient has had constipation, excessive urination, and fatigue for the past several months. His medical history is notable for a kidney stone a year ago that passed with intravenous and oral hydration. The patient does not take any prescription medications, and does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. His temperature is 37.2 C (98.9 F) and blood pressure is 130/76 mm Hg. Examination shows tenderness, erythema, and swelling of the right knee. The remainder of the examination is unremarkable. Laboratory results are as follows:
Complete blood count Hemoglobin 13 g/dL Platelets 240,000/mm3 Leukocytes 13,000/mm3 Serum chemistry Sodium 138 mEq/L Potassium 4.2 mEq/L Urea nitrogen 18 mg/dL Creatinine 1.0 mg/dL Calcium 11 mg/dL Glucose 90 mg/dL Arthrocentesis is performed. Which of the following is most likely to be found on synovial fluid assessment in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 40
8. Question
A 40-year-old man is intubated and receiving mechanical ventilation after being found unresponsive on the floor of his apartment. The patient is sedated and initiates no spontaneous breaths. The ventilator triggers 14 breaths/min, each delivering 500 mL of tidal volume. Because of difficulty in ventilating the patient’s airway, an inspiratory hold maneuver is performed to further evaluate his respiratory mechanics. During this maneuver, the ventilator is paused for 2 seconds after the entire tidal volume is delivered. The pressure at the mouthpiece, measured when there is no flow, is found to be elevated.

The measured pressure most likely reflects which of the following?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 40
9. Question
A 28-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to bilateral upper extremity weakness and abdominal pain. The patient has had progressive weakness of the upper extremities for 2 days and severe, diffuse, poorly localized abdominal pain for 1 day. Temperature is 37.3 C (99.1 F), blood pressure is 148/86 mm Hg, and pulse is 112/min. On physical examination, the patient appears restless and is diaphoretic. There is no scleral icterus. The abdomen is soft and nontender, with no organomegaly, guarding, or rebound tenderness. Bowel sounds are decreased. Neurological examination shows normal cranial nerves, weakness of the proximal upper extremity muscles, and loss of the biceps and triceps reflexes on both sides. Laboratory results are as follows:
Complete blood count
Hemoglobin
13 g/dL
Platelets
280,000/mm3
Leukocytes
11,000/mm3
Serum chemistry
Sodium
130 mEq/L
Potassium
4.2 mEq/L
Chloride
96 mEq/L
Bicarbonate
24 mEq/L
Creatinine
0.8 mg/dL
Liver function studies
Total bilirubin
0.8 mg/dL
Alkaline phosphatase
50 U/L
Aspartate aminotransferase (SGOT)
32 U/L
Alanine aminotransferase (SGPT)
36 U/L
Urinalysis
Protein
none
Blood
negative
White blood cells
0-1/hpf
Red blood cells
0-1/hpf
Casts
none
Urobilinogen
positive
Which of the following is most likely to yield the diagnosis in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 40
10. Question
A 54-year-old man comes to the office due to shortness of breath at night. He has also felt weak but has had no dyspnea on exertion or leg swelling. His wife adds that the patient has had occasional cough while eating and that his speech is slightly slurred. He has no chronic medical conditions and is a lifelong nonsmoker. Vital signs are within normal limits. BMI is 25 kg/m2. On physical examination, the soft palate and uvula are completely visualized. The tongue is mildly atrophic with visible fasciculations. The lungs are clear on auscultation and heart sounds are normal. The abdomen is flat and moves outward during expiration. There is no extremity edema. Chest x-ray shows elevated hemidiaphragms but no parenchymal opacities. Compared to a healthy individual’s tests, this patient’s pulmonary function testing is most likely to reveal which of the following findings?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 40
11. Question
A 24-year-old man is brought to the office by his parents due to hand shaking and involuntary movements, which have progressively worsened over the last 6 months. A year ago, he was diagnosed with depression and treated with fluoxetine for 5 months but stopped the medication and did not follow up with his psychiatrist. His medical history is otherwise unremarkable. The patient has smoked cigarettes intermittently in the past but does not drink alcohol or use illicit drugs. He dropped out of college and has worked as a delivery man for the last several years. Blood pressure is 122/82 mm Hg supine and 120/84 mm Hg standing. Physical examination reveals clear breath sounds and no cardiac murmurs. The liver is enlarged, firm, and nontender, and the spleen is not palpable. There is tremor of both hands that increases with activity. Occasional rapid, jerky contractions of the distal extremities are also seen. Laboratory results are as follows:
Total bilirubin
1.9 mg/dL
Direct bilirubin
0.9 mg/dL
Alkaline phosphatase
31 U/L
Aspartate aminotransferase
276 U/L
Alanine aminotransferase
130 U/L
Prothrombin time
12.0 sec
Viral hepatitis panel is negative. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 40
12. Question
A 46-year-old man is being evaluated for a gait disorder. He was referred by social workers due to frequent falls. His symptoms began gradually about a year ago and have become progressively worse. The patient’s history is notable for alcohol use disorder, and he is currently experiencing homelessness, with sporadic stays in a nearby shelter. On examination, he has a broad-based, unsteady gait. A single tap on his patellar tendon elicits persistent, slow, back-and-forth swinging of the leg. Nystagmus and truncal ataxia are also present. Which of the following additional findings would most likely be seen in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 40
13. Question
A 44-year-old car mechanic comes to the office due to a 4-week history of right elbow pain. The pain is worse when grasping tools with the right hand and is not relieved by over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. He has had no acute trauma to the elbow. On examination, the elbow is not swollen and has full range of motion. There is tenderness on palpation around the lateral distal humerus. Pain is reproduced when testing grip strength and with resisted wrist extension. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 40
14. Question
A 75-year-old man is brought to the emergency department from home after being found unresponsive by his son. His medical history is significant for coronary artery disease with coronary stenting 2 years ago, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and stroke. He was hospitalized 2 months ago with pneumonia and upper gastrointestinal bleeding, during which time he received intravenous antibiotics and a transfusion of 4 units of packed red blood cells. In the emergency department today, temperature is 39.1 C (102.4 F), blood pressure is 70/40 mm Hg, pulse is 120/min, respiratory rate is 32/min, and oxygen saturation is 79% on room air. Laboratory results are notable for leukocytosis but are otherwise unremarkable. Chest x-ray reveals a new right upper lobe infiltrate. He is treated with normal saline, antibiotics, vasopressors, and mechanical ventilation. The next day, laboratory analyses reveal the following:
Hemoglobin 9.5 mg/dL Leukocytes 15,000/mm3 Platelet 120,000/mm3 Sodium 137 mEq/L Potassium 4.1 mEq/L Chloride 100 mEq/L Bicarbonate 19 mEq/L Blood urea nitrogen 51 mg/dL Creatinine 2.1 mg/dL Bilirubin, total 1.2 mg/dL Aspartate aminotransferase 3,720 units/L Alanine aminotransferase 3,250 units/L Alkaline phosphatase 162 mEq/L Which of the following most likely accounts for the abnormal liver function panel?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 40
15. Question
A 35-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department due to 3 days of progressive nausea, anorexia, malaise, abdominal pain, and lethargy. The patient is a chronic carrier of hepatitis B virus and has not received any treatment. She has a history of injection drug use and completed a rehabilitation program 2 years ago, but recently started using drugs again. She drinks alcohol but does not use tobacco. Her temperature is 37.8 C (100.2 F), blood pressure is 106/64 mm Hg, and pulse is 114/min. Mild tender hepatomegaly is present. Laboratory testing shows markedly elevated serum aminotransferase levels and a positive serum hepatitis D antigen. Acute liver failure due to hepatitis D virus superinfection is suspected. Which of the following is required to make a diagnosis of acute liver failure in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 40
16. Question
A 12-year-old girl is brought to the office by her father for headaches for the past 6 months. She describes a “squeezing” pain that is bilateral and lasts from 15 minutes to several hours until she goes to bed. A few times she has seen “squiggly lines” in her vision before the headaches occur. The patient has had no photophobia or nausea. The father estimates she has headaches 2-3 times per month. The patient says she has them at least twice per week; they sometimes begin when she is in class, but they most often occur after school before her parents come home from work. If she tells her parents, they give her ibuprofen, which sometimes helps. The patient is a competitive swimmer and has 3-4 practices per week; she attends practice if she has a headache, although this makes the headache worse. Vital signs are normal and neurological examination including funduscopy is unremarkable. What is the best next step in management of this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 40
17. Question
A 20-year-old previously healthy woman comes to the office due to intermittent diarrhea and abdominal pain over the past several months. The patient has had bouts of diarrhea alternating with normal bowel movements, but lately the diarrhea has become more persistent. She reports 4-6 loose, brown stools each day, which awaken her at night. The diarrhea is associated with crampy abdominal pain in both lower quadrants that subsides after a bowel movement. The pain and diarrhea frequently occur after eating. There are also days when she feels constipated and passes only a small amount of mucus. The patient has had no hematochezia, melena, or weight changes. There is no family history of gastrointestinal diseases. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or recreational drugs. Vital signs are normal. Physical examination, including abdominal and rectal examination, shows no abnormalities. Stool testing for occult blood is negative, and blood cell counts and serum chemistry studies are within normal limits. C-reactive protein is normal. Serologic testing for celiac disease is negative. Further testing may be indicated in this patient due to which of the following findings?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 18 of 40
18. Question
A 59-year-old man comes to visit a friend in the hospital and collapses in the parking lot. He had been feeling unwell all day due to vague chest discomfort. A bystander witnesses his collapse, finds no pulse, and immediately calls for help. The elapsed time to which of the following is the most important factor for survival in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 40
19. Question
A 58-year-old man is evaluated for increasing left shoulder pain over the past several months. The pain is worse with movement. The patient stopped playing golf 2 months ago due to the pain, and lately it is also limiting his daily activities. He has had no shoulder trauma or pain in other joints. Medical history includes hypertension and hyperlipidemia. Left shoulder examination shows decreased range of motion in external rotation and abduction due to pain. Injection of lidocaine in the subacromial space relieves the pain but active and passive range of motion remain limited. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 40
20. Question
A 42-year-old man who recently emigrated from Northern Africa comes to the clinic due to a 1-month history of abdominal pain and watery diarrhea. He has also had a skin rash for the last 2 months that gets worse with sun exposure. In addition, the patient has felt depressed recently and has loss of appetite with mild weight loss. Medical history is notable for latent tuberculosis, for which he is currently taking daily isoniazid. The patient takes no other medications and does not use tobacco, alcohol, or recreational drugs. He is vegetarian, and his diet has consisted mostly of corn and other cereal grains. On examination, there is a pigmented scaly skin rash in the malar distribution of his face, on his neck, and on the back of his hands. He also has mild, diffuse abdominal tenderness. Neurologic examination, including distal sensation and gait, is normal. Liver function tests are normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 21 of 40
21. Question
A 54-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to several hours of severe epigastric abdominal pain. The patient began having mild colicky upper abdominal pain after dinner last night and took acetaminophen before going to bed. In the night, the patient awoke with severe abdominal pain radiating to her back. She has also had nausea and several episodes of vomiting. The patient has a history of occasional upper abdominal pain after eating but has never had such severe symptoms. She has no other medical issues and takes no medications. Temperature is 37.6 C (99.6 F), blood pressure is 110/66 mm Hg, pulse is 118/min, and respirations are 24/min. The patient appears to be in moderate distress. Mucous membranes are dry. The abdomen is distended with marked epigastric tenderness. Bowel sounds are decreased. Laboratory results are as follows:
Complete blood count
Hematocrit
48%
Leukocytes
18,800/mm3
Liver function studies
Total bilirubin
2.2 mg/dL
Alkaline phosphatase
370 U/L
Lipase
2,192 U/L
Which of the following sets of renal findings are most expected in this patient?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 22 of 40
22. Question
A 65-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to lower extremity swelling and a 9.1-kg (20.1-lb) weight gain over the last month. He also reports some shortness of breath at night. The patient has a history of hypertension and coronary artery disease and underwent coronary artery bypass graft surgery 10 years ago. The patient does not smoke or use recreational drugs. Temperature is 36.7 C (98.1 F), blood pressure is 140/92 mm Hg, pulse is 98/min, and respirations are 18/min. Examination shows jugular venous distension. Breath sounds are decreased at the bilateral bases. The point of maximal impulse is laterally displaced. S1 and S2 are normal, and a II/VI holosystolic murmur is present at the apex. There is 3+ pretibial edema bilaterally. Laboratory results are as follows:
Serum chemistry
Sodium
136 mEq/L
Potassium
4 mEq/L
Chloride
106 mEq/L
Bicarbonate
22 mEq/L
Blood urea nitrogen
50 mg/dL
Creatinine
2.0 mg/dL
Calcium
8.4 mg/dL
Glucose
100 mg/dL
Urinalysis
Specific gravity
1.022
Protein
none
Blood
negative
White blood cells
1-2/hpf
Red blood cells
1-2/hpf
Casts
none
Chest x-ray reveals an enlarged cardiac silhouette and pulmonary vascular congestion. The patient is treated with intravenous furosemide for 4 days, with a return to his baseline weight and resolution of his edema. Serum chemistry shows an improvement in creatinine to 1.1 mg/dL. Which of the following is the most likely mechanism by which this drug therapy led to improved renal function?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 23 of 40
23. Question
A 56-year-old man comes to the office due to burning pain in his feet. The patient initially began experiencing pins and needles in his toes several months ago, which gradually worsened to involve the entire foot. Lately, he has had burning and cramping pain daily in both feet, which is more pronounced at night. The patient has had occasional back pain but has no chronic medical conditions and takes no medications. He is a construction worker and is frequently exposed to vibrating machinery. He does not smoke but drinks 4-6 beers daily and more on the weekends. Vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows loss of bilateral ankle reflex and impaired light touch and vibration sensation in both feet. The remainder of the examination reveals no abnormalities. Hemoglobin A1c and methylmalonic acid levels are within normal limits. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s symptoms?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 24 of 40
24. Question
A 58-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after being found lethargic by his wife, who also discovered a suicide note. The patient has a history of coronary artery disease and hypertension. Temperature is 37.7 C (99.9 F), blood pressure is 76/40 mm Hg, pulse is 40/min, and respirations are 12/min. Examination shows diffuse bilateral wheezing. Extremities are cold and clammy. ECG shows profound sinus bradycardia with first-degree atrioventricular block. The patient is given intravenous fluids and atropine; however, the bradycardia and hypotension do not improve. In addition to ensuring adequate oxygenation, which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 25 of 40
25. Question
A 35-year-old man comes to the office due to concern that his HIV medication is no longer working. Over the last 6 weeks, the patient has had intermittent fevers and awakened several times drenched in sweat. He has not used injection drugs since he was diagnosed with HIV a year ago, and he lives in a house with other individuals recovering from substance use disorder. The patient takes antiretroviral therapy and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Temperature is 37.9 C (100.2 F), blood pressure is 126/72 mm Hg, and pulse is 102/min. Physical examination reveals several enlarged cervical, supraclavicular, and epitrochlear lymph nodes that are rubbery and mobile. Cardiopulmonary examination is normal, and no organomegaly is present on abdominal examination. There is no rash. Chest x-ray reveals an enlarged cardiac silhouette. Current CD4 count is 208/mm3 and the viral load is undetectable. Which of the following underlying pathogens is most likely responsible for this patient’s symptoms?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 26 of 40
26. Question
A 17-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department due to acute abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. She has no chronic medical conditions and has had no surgery. The patient has had irregular menstruation and is not sexually active. Family history is significant for deep venous thrombosis following knee replacement in her mother, who takes apixaban. Temperature is 38.3 C (101 F). BMI is 18 kg/m2. Physical examination shows right lower quadrant abdominal tenderness. CT scan of the abdomen reveals acute appendicitis, and laparoscopic appendectomy is planned. Preoperative laboratory studies demonstrate a platelet count of 400,000/mm3. Coagulation study results are as follows:
Prothrombin time
12 sec
International Normalized Ratio (INR)
1.2 (normal: 0.8-1.2)
Activated partial thromboplastin time
52 sec
Thrombin time
15 sec (normal: 14-19 sec)
Mixing the patient’s plasma sample with normal plasma fails to correct the coagulation abnormalities. Which of the following best explains this patient’s coagulation study results?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 40
27. Question
A 60-year-old man is brought to the emergency department due to fever, chills, and confusion. The patient was fishing in the ocean yesterday and cut his foot on a jagged rock while wading through shallow water. He was unable to clean the wound right away, and overnight, it became increasingly red and painful. The patient was awakened several times by fever and chills, and this morning, his wife found him disoriented. Medical history includes hypertension. Temperature is 38.8 C (101.8 F), blood pressure is 86/62 mm Hg, pulse is 118/min, and respirations are 24/min. On physical examination, the patient is in moderate distress. Heart sounds are rapid and regular with no murmurs. The lungs are clear to auscultation. Breathing is fast and shallow. The right foot shows a laceration with purulent drainage and erythema spreading to the midshin. The results of arterial blood gas testing on room air are as follows:
pH
7.08
PaO2
86 mm Hg
PaCO2
42 mm Hg
Serum bicarbonate
12 mEq/L
Which of the following best describes the acid-base status of this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 28 of 40
28. Question
A 42-year-old man is brought to the emergency department due to weakness. The patient drinks alcohol daily and has been binge drinking for the past 2 days. He also used cocaine the previous night. This morning, the patient stumbled and fell several times while trying to get to the bathroom. He has no other medical problems and takes no medications. Temperature is 37 C (98.6 F), blood pressure is 160/100 mm Hg, pulse is 102/min, and respirations are 18/min. Oxygen saturation is 96% on room air. Physical examination shows mildly dilated pupils. The oropharynx is clear. There is no jugular venous distension. Cardiopulmonary examination is normal. The abdomen is soft and nontender. Bilateral thighs and calves are mildly swollen and tender. Lower extremity muscle strength is decreased, but sensation to touch and vibration is normal. Upper extremity examination shows no abnormalities. Over the next several days, this patient is at greatest risk for which of the following complications of his current condition?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 29 of 40
29. Question
A 34-year-old woman comes to the office for evaluation of skin lesions. For the past year, she has noticed darkening and thickening of the skin over her neck and groin areas. These areas occasionally feel itchy. Blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg. Skin examination findings are shown in the image below.

Similar hyperpigmented, velvety lesions are found on the axilla and groin. This patient’s skin manifestations are most likely associated with which of the following underlying conditions?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 30 of 40
30. Question
A 65-year-old man is evaluated for right-hand clumsiness that has slowly worsened over the past several months. Medical history is significant for hypertension and end-stage renal disease, for which he undergoes hemodialysis 3 times a week. The patient is retired and not physically active. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or recreational drugs. Blood pressure is 130/90 mm Hg and pulse is 80/min. BMI is 20 kg/m2. Examination of the right upper extremity shows decreased sensation over the fourth and fifth digits and the medial hand; grip strength and wrist flexion are weaker compared to the left side. Overall muscle mass and tone are decreased in all 4 extremities. Which of the following is the most likely site of nerve injury?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 31 of 40
31. Question
A 30-year-old man comes to the office due to 2 months of lower extremity swelling and skin lesions on his groin. The lesions are not painful. Review of systems is positive for frequent loose stools and a 10% weight loss from baseline. The patient used intravenous heroin in the past and was hospitalized 3 years ago for right upper extremity cellulitis near an injection site. Temperature is 37.2 C (99 F), blood pressure is 132/78 mm Hg, and pulse is 92/min. BMI is 22 kg/m2. Oral mucosa appears normal. Bilateral inguinal lymphadenopathy and mild lower extremity edema are present. Skin examination of the groin region is shown below:

This patient would benefit most from which therapy?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 32 of 40
32. Question
A 75-year-old woman comes to the emergency department for shortness of breath. Her family reports she has been having difficulty breathing for the last few nights. About an hour ago, the patient’s condition suddenly deteriorated and she developed significant respiratory distress. She has had no fever or cough but has been out of her regular medications for a week. Medical history is significant for hypertension, coronary artery disease, and heart failure. Temperature is 36.7 C (98.1 F), blood pressure is 205/110 mm Hg, pulse is 112/min, and respirations are 32/min. Pulse oximetry is 89% on high-flow oxygen. The patient is awake but in distress and able to speak only in 1-word sentences. Bilateral crackles and an S3 gallop are present. She has 3+ pitting edema in her bilateral lower extremities. Noninvasive positive pressure mechanical ventilation is initiated. The beneficial effects of positive pressure ventilation in this patient are most likely through which of the following physiologic changes?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 33 of 40
33. Question
A 57-year-old man who just returned from a cruise to the Bahamas comes to the emergency department with fever, nonproductive cough, and shortness of breath for the past 2 days. He has also had a headache, abdominal pain, and diarrhea for a day. The patient has a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus and has smoked a pack of cigarettes daily for 20 years. He does not use alcohol or illicit drugs. His temperature is 39.2 C (102.6 F), blood pressure is 110/65 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 18/min. The patient’s pulse oximetry shows 97% on room air. Lung examination shows crackles bilaterally. The abdomen is soft and nontender. The patient seems confused at times during the examination. His serum glucose is normal; serum sodium is 128 mEq/L. Chest x-ray demonstrates bilateral interstitial infiltrates. He is admitted to the ward. Which of the following antibiotics should be given to this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 34 of 40
34. Question
A 60-year-old man comes to the office after he was found to have a “low blood count” when attempting to donate blood. The patient is in his usual state of health and feels well. He has no chronic medical problems but has been treated for pneumonia twice during the past year. The patient takes no medications and does not use tobacco or alcohol. Temperature is 37 C (98.6 F), blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, and pulse is 76/min. Physical examination reveals mucosal pallor. There are no enlarged lymph nodes. The abdomen is soft and nontender. The spleen tip is palpable 5 cm below the left costal margin; the liver is normal in size. Stool guaiac is negative. Complete blood count results are as follows:
Hemoglobin
9.6 g/dL
Mean corpuscular volume
83 fL
Platelets
130,000/mm3
Leukocytes
14,000/mm3
Peripheral blood smear shows predominant lymphocytes with features as seen in the image below.
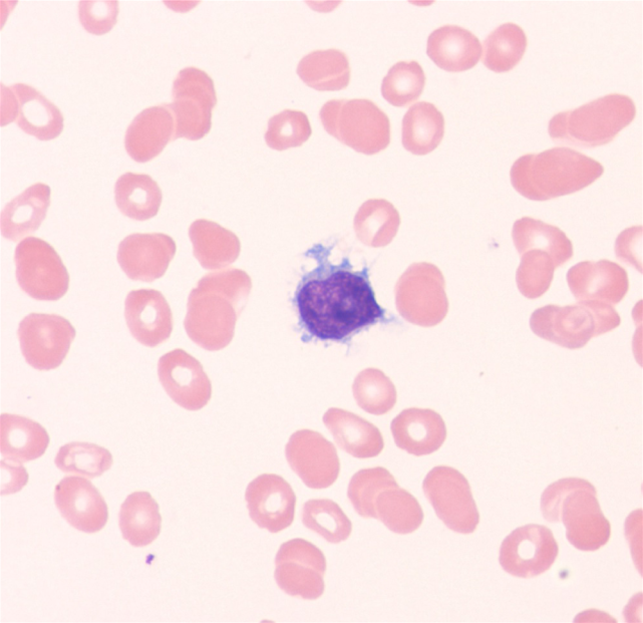
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 35 of 40
35. Question
A 68-year-old woman with a history of advanced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease comes to the emergency department due to increased shortness of breath and cough for 12 hours. She took 2 extra nebulizer treatments at home with no relief of symptoms. She has no fever, nausea, vomiting, or hemoptysis. The patient has been oxygen dependent for the last 2 years. She has a 45-pack-year smoking history and quit about 6 years ago. Medications include tiotropium daily, fluticasone/salmeterol twice daily, and albuterol by metered-dose inhaler or nebulizer as needed. Temperature is 36.7 C (98.1 F), blood pressure is 110/65 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 28/min. The patient appears dyspneic and in moderate distress. She is given intravenous antibiotics, methylprednisolone, and 2 treatments of nebulized ipratropium with albuterol. Following these measures, the patient remains dyspneic and uses accessory muscles of respiration but is alert and follows commands. On 4 L/min O2, her pulse oximetry is 89%, and arterial blood gas shows pH of 7.30, PCO2 of 63 mm Hg, and PO2 of 54 mm Hg. Chest x-ray, shown in the image below, demonstrates hyperinflation:

Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 36 of 40
36. Question
A 64-year-old woman is brought to the office by her spouse due to cognitive impairment. The patient has been mildly forgetful over the past 2 years, with further significant decline in the last 3 months. She performs most daily activities independently but must be reminded frequently to perform basic self-care. The patient has also become unsteady, and she has had 2 near falls in the last 3 months. She still enjoys spending time with family and friends. The patient has a 6-year history of HIV infection and takes antiretroviral therapy. Her most recent CD4 cell count was 600/mm3 3 months ago. Other medical history includes hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Temperature is 37.1 C (98.8 F), blood pressure is 140/82 mm Hg, and pulse is 80/min. On physical examination, the patient is oriented to time, place, and person, but there is short-term memory impairment. Mild weakness of the left-sided extremities and a pronator drift of the left arm are present. She is unsteady in the Romberg position with her eyes closed. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s cognitive impairment?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 37 of 40
37. Question
A 54-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to double vision and a droopy eyelid. The patient began seeing 2 side-by-side images while watching television last night. She attributed the symptoms to tiredness and went to bed. The vision disturbance was persistent on waking up today, and the patient also found her right eyelid was drooping. The diplopia is worse when looking toward the left and is not associated with headache, nausea, dizziness, or focal weakness or numbness. Physical examination shows ptosis of the right eye. Adduction and upward gaze are impaired on the right side. Pupils are 2 mm on the left and 5 mm on the right, and both are reactive to light. Examination of other cranial nerves is unremarkable. Upper and lower extremity strength, deep tendon reflexes, and sensation are normal. Noncontrast CT scan of the head is normal. Which of the following is the best next step in evaluation of this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 38 of 40
38. Question
A 65-year-old woman comes to the office due to a 2-month history of fatigue and weight gain. The patient has rheumatoid arthritis, peptic ulcer disease, and hypertension. She takes hydrochlorothiazide and acetaminophen. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or recreational drugs. Blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 14/min. Generalized edema is noted on physical examination. The liver is palpated 5 cm below the costal margin. Urinalysis shows 4+ proteinuria. Ultrasonography reveals bilateral kidney enlargement. Renal biopsy is performed. Which of the following is the most likely finding on pathologic examination?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 39 of 40
39. Question
A 40-year-old woman comes to the office due to daily headaches and facial pain for the past several months. The pain involves the temporal and periorbital region, affects the right side more than the left, is dull, and waxes and wanes. It is often worse toward the end of the day, and the patient gets a heavy and tired feeling in her jaws while eating dinner. Current medications are a multivitamin daily and ibuprofen as needed. She is a research professor and describes her work as stressful. The patient does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows normal pupils and no facial droop. Facial sensation is normal bilaterally and there is mild tenderness in the right masseter muscle. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 40 of 40
40. Question
A 34-year-old man is brought to the emergency department due to confusion. The patient recently lost his job and moved in with his parents yesterday because he could no longer afford housing. Today, his mother found him disoriented and unsteady. He has no known chronic medical conditions and takes no medications. Temperature is 38.5 C (101.3 F), blood pressure is 164/90 mm Hg, pulse is 108/min, and respirations are 22/min. The patient appears restless and is constantly picking at the bed linens, yelling, “Get these bugs off me.” The lungs are clear on auscultation, and cardiac examination is unremarkable with the exception of regular tachycardia. The abdomen is soft and nontender. No extremity edema is present. Laboratory results are as follows:
Complete blood count
Hemoglobin
14.8 g/dL
Mean corpuscular volume
104 µm3
Platelets
300,000/mm3
Leukocytes
11,000/mm3
Serum chemistry
Sodium
146 mEq/L
Potassium
3.1 mEq/L
Magnesium
1.8 mg/dL
Phosphorus
2.4 mg/dL
Creatinine
0.8 mg/dL
Which of the following would be most helpful to improve this patient’s current condition?
CorrectIncorrect
